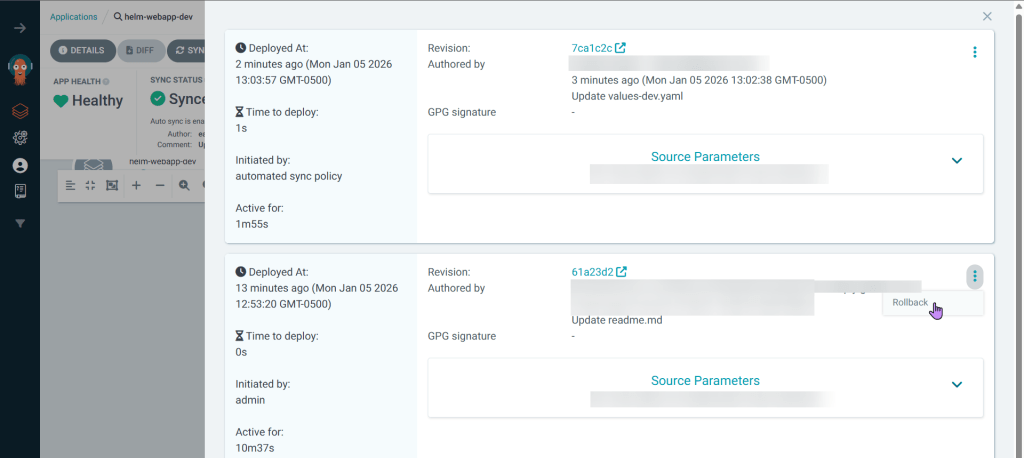
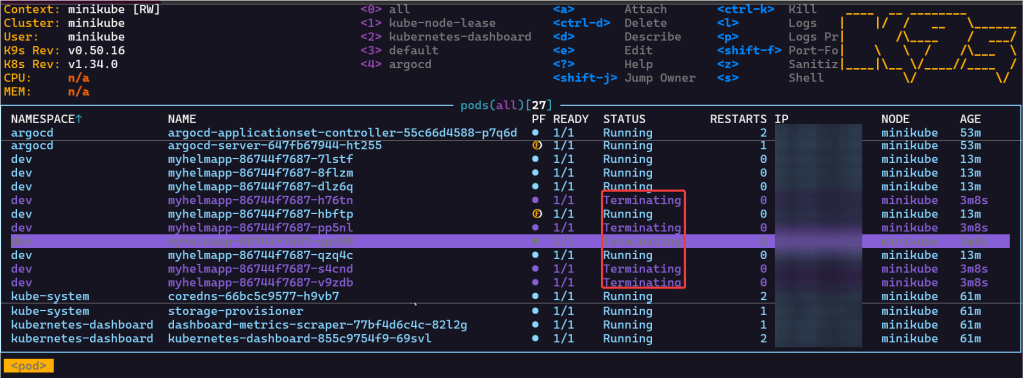
Series of blog posts show progress of updating/adding to EKS Cluster
Below are links for details:
- Github Repo:
- Terraform:
- AWS:
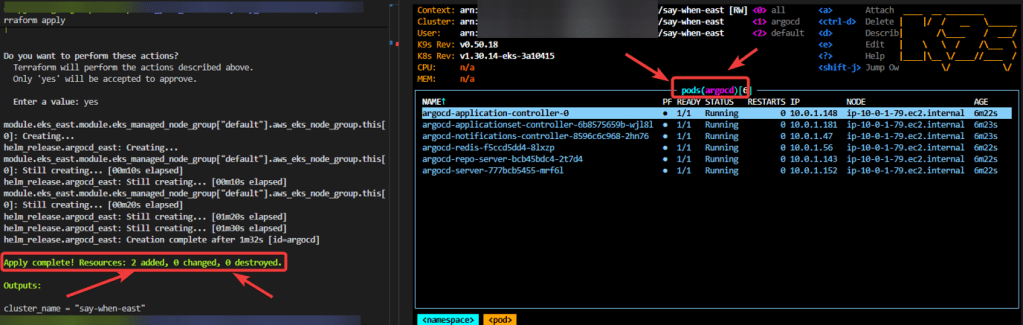
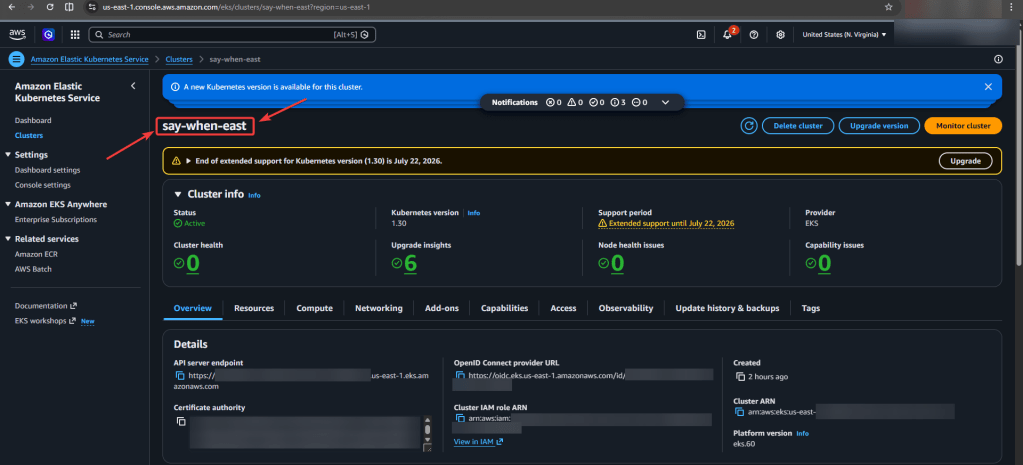
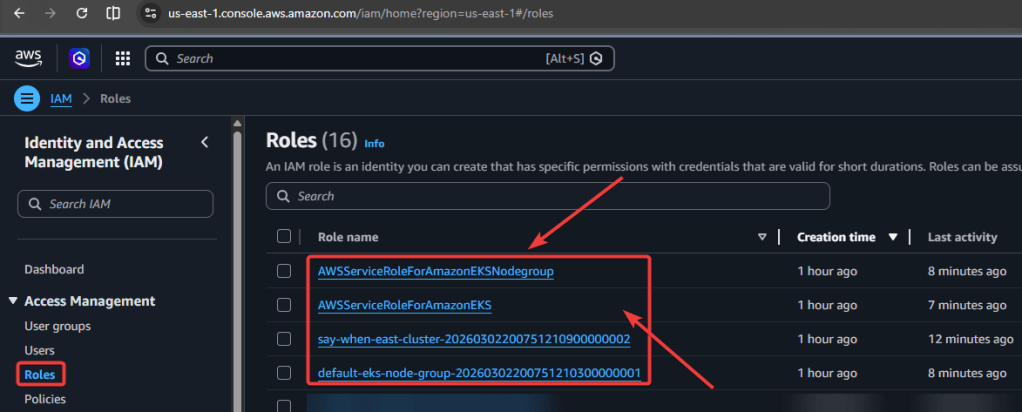
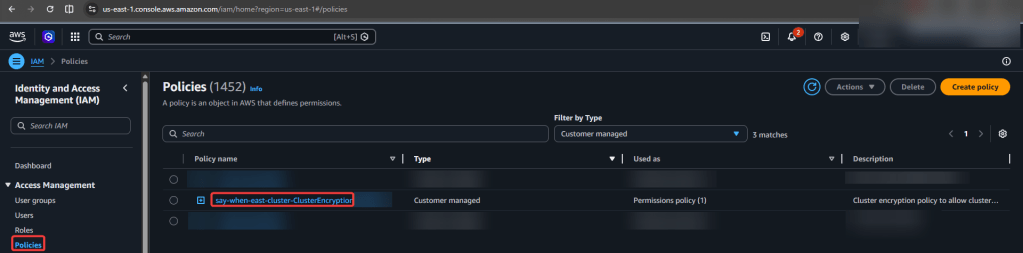


Series of blog posts show progress of updating/adding to EKS Cluster
Below are links for details:










View Code here for details w/this dope link:
Commands below:
$ kubectl create namespace metrics$ helm repo add metrics-server https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/metrics-server/$ helm repo update$ helm upgrade --install metrics-server metrics-server/metrics-server \ --namespace metrics \ --set args={--kubelet-insecure-tls}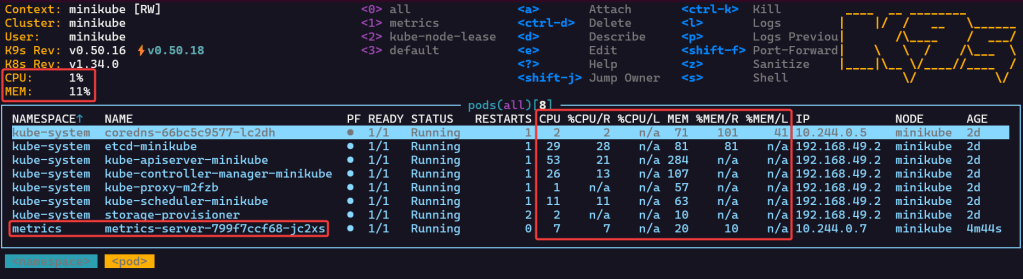

View Code here for details w/this dope link:
Below is a summary of steps:
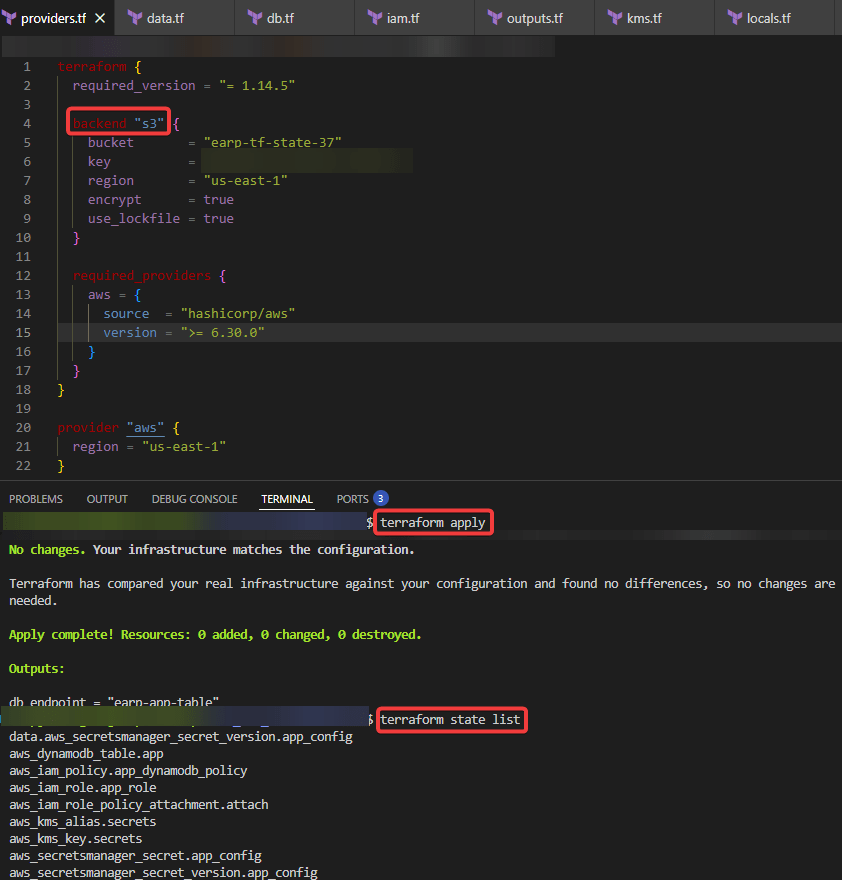
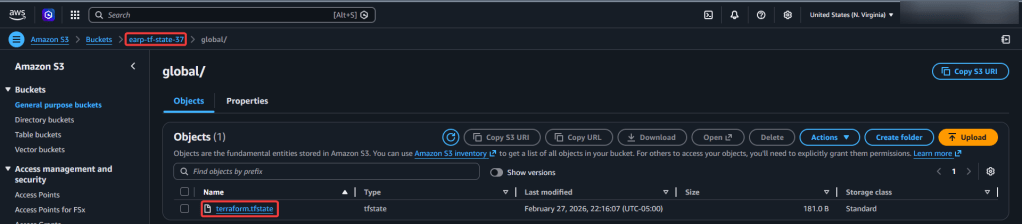
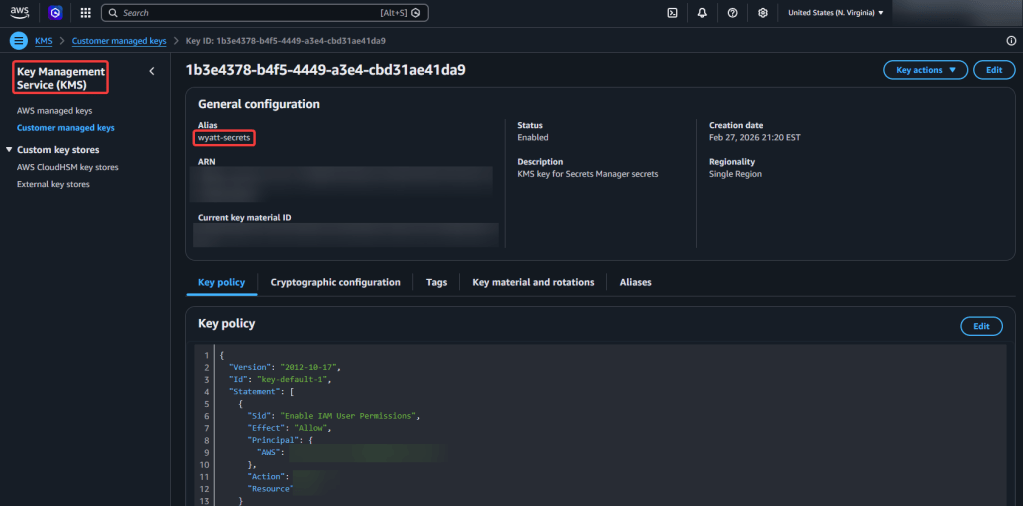

View Code here for details w/this dope link:
Below are details into to use Terraform in creating a tool to upload a medical professional notes into AWS & summarize your notes auto-magically, w/the help of HIPPA the Hippo!
Contents of Tables:
General Steps followed in my brain:
##############################################
##############################################
User uploads audio → S3
↓
Transcribe Medical job
↓
Transcript saved to S3
↓
Lambda calls Comprehend Medical
↓
Extracted entities saved to S3
Step 1 – Upload audio file w/commands you might need:
sudo apt updatesudo apt install ffmpegffmpeg -versionffmpeg -i "S3-AWS-Medical.m4a" -ar 16000 -ac 1 S3-AWS-Medical.wavterraform initterraform fmtterraform validateterraform planterraform applyaws s3 cp S3-AWS-Medical.wav s3://your-input-bucket-name/Step 2 – Check various AWS locations (s3, lambdas, roles, etc):
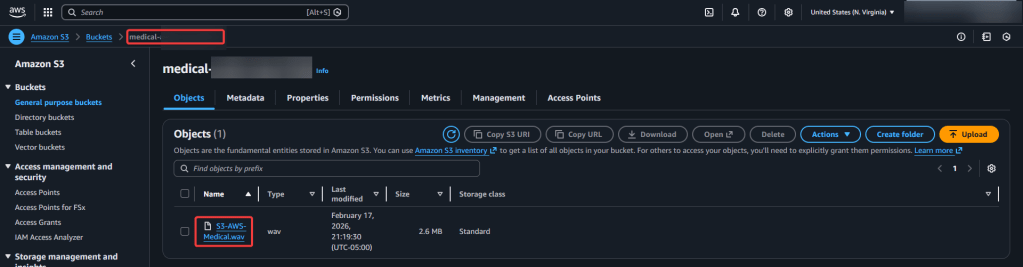
Step 3 – Run Lambda.py script:
python3 transcribe.py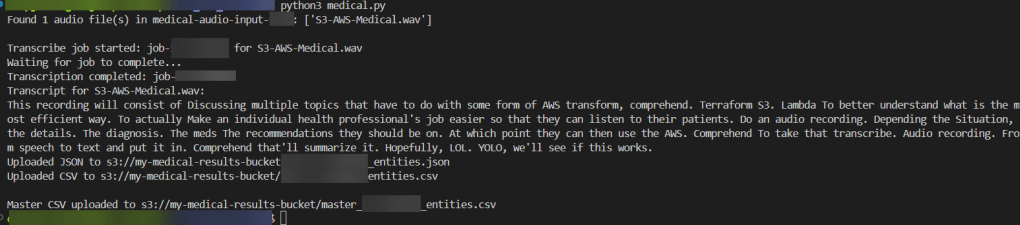
Step 4 – Confirm in AWS Transcribe Medical & S3 Buckets of data:
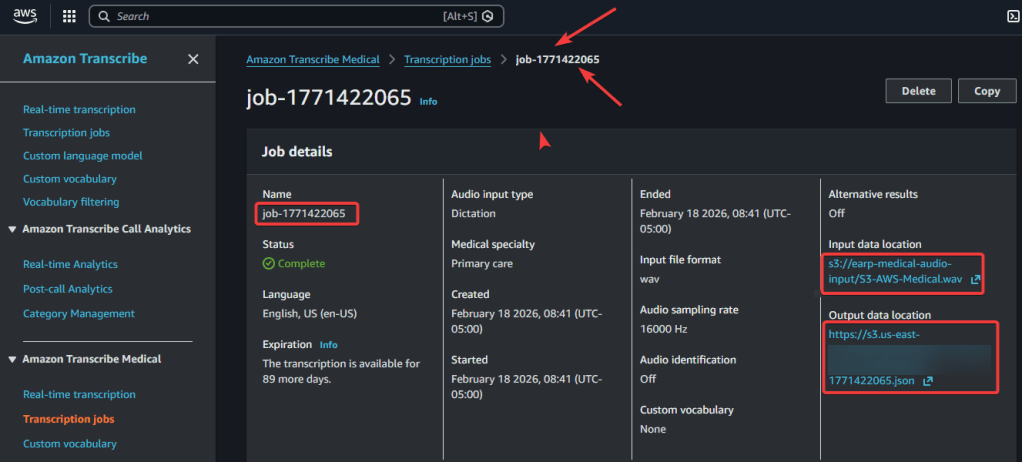
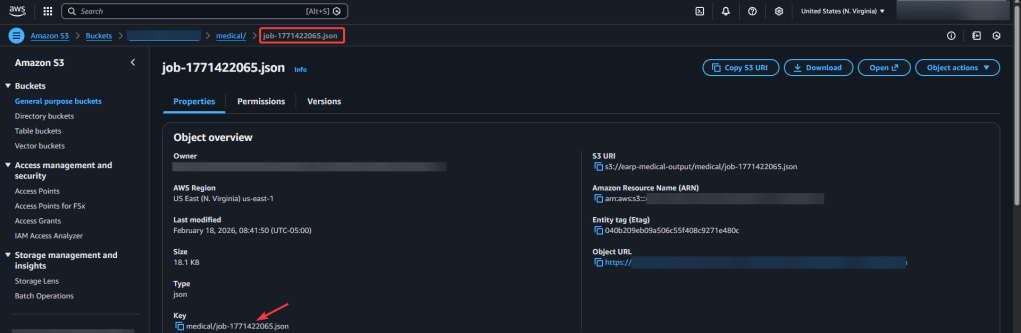
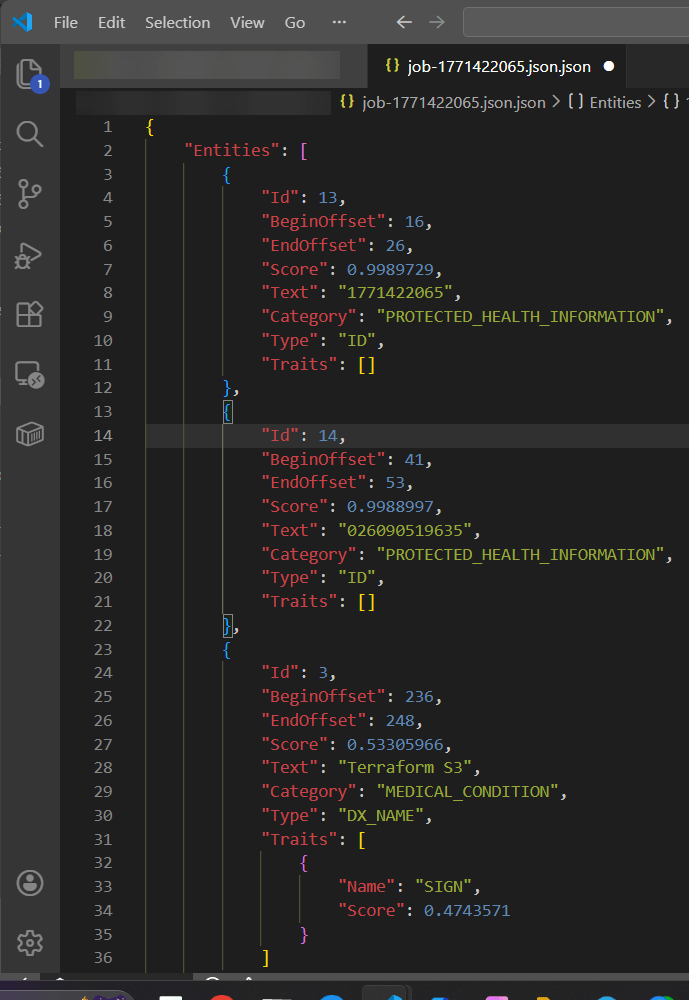
Step 5.1 AWS Comprehend Medical – Create Job:
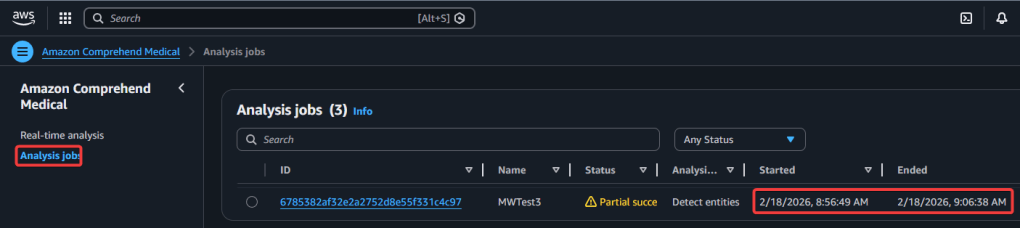
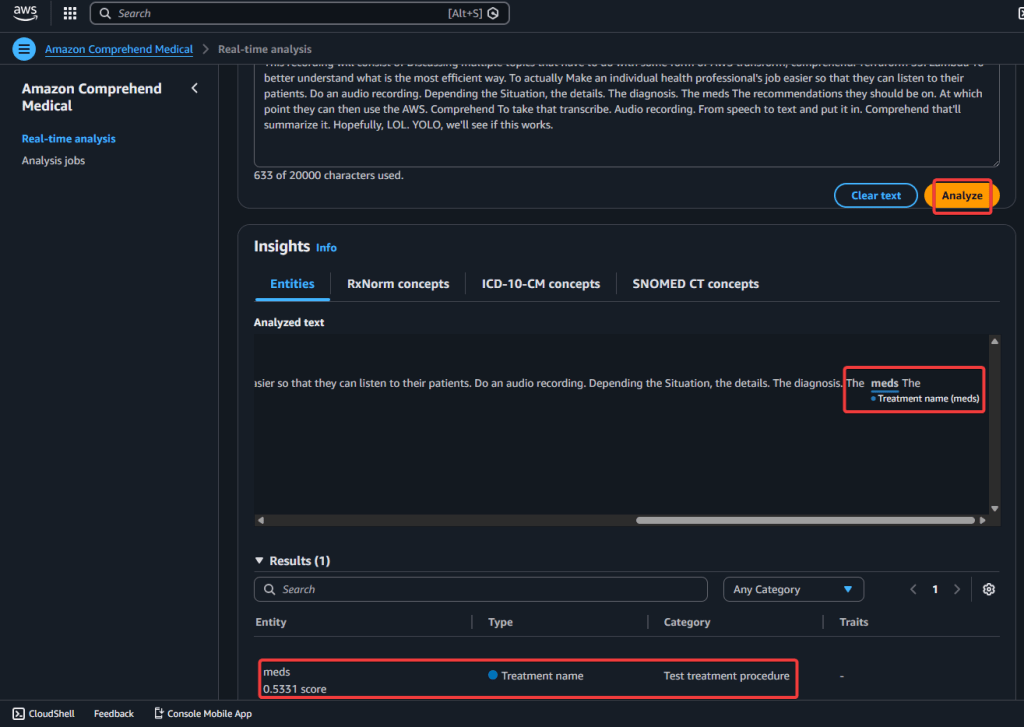
Step 5.2 AWS Comprehend Medical – Real-Time Analysis:
View Zaaa Code here:
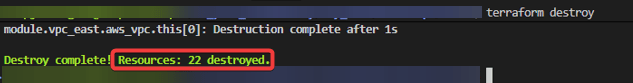
git initgit add .git statusgit commit -m "First commit for AWS Transcribe + Comprehend Medical w/Terraform."git remote add origin https://github.com/earpjennings37/aws-medical-tf.gitgit branch -M Maingit push -u origin maingit checkout -b update-readmegit branchgit statusgit add .git commit -m "updated-readme"git push -u origin update-readme
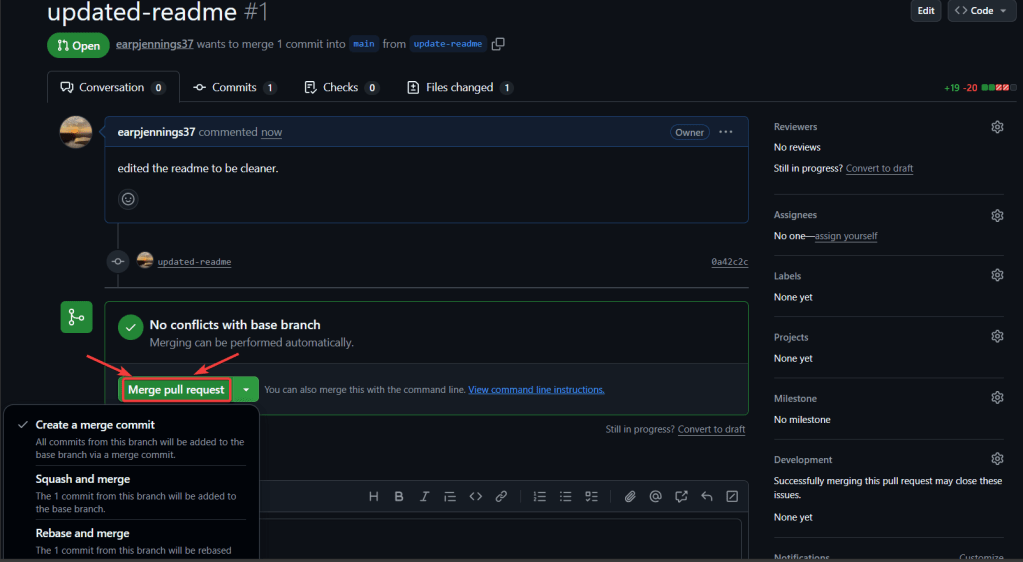
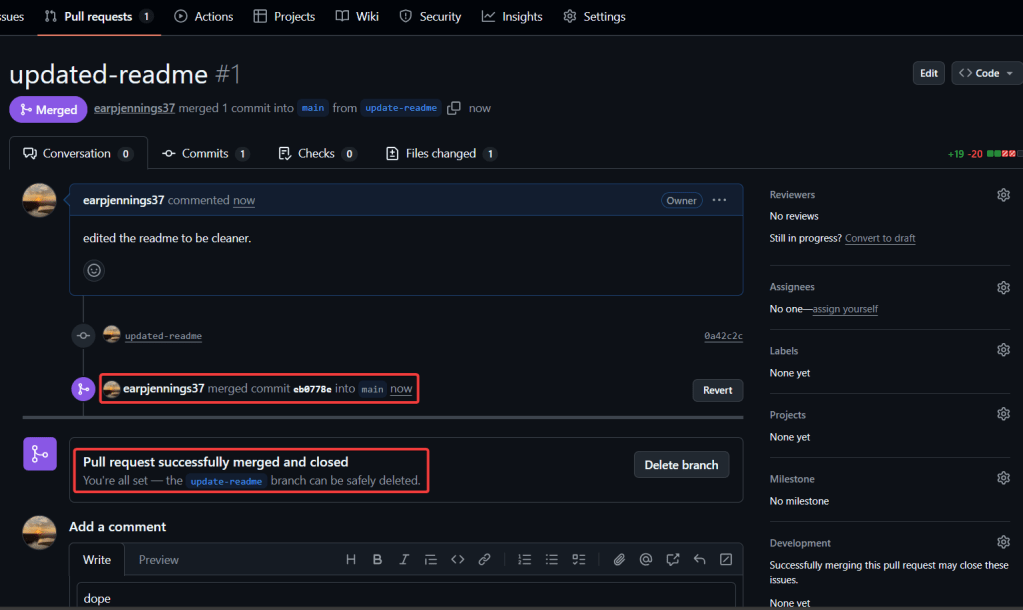

You like kubectl ya? Well how about slappin some “agentic-ai” on that cli & see what happens. Lets run it, see below for 4 examples.
Pre-Reqxzz aka 3 stepzz:
Commands to get goin:
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/kubectl-ai/main/install.sh | bashexport GEMINI_API_KEY=your_api_key_herekubectl-ai --helpkubectl-ai modelskubectl-ai --model gemini-2.5-flash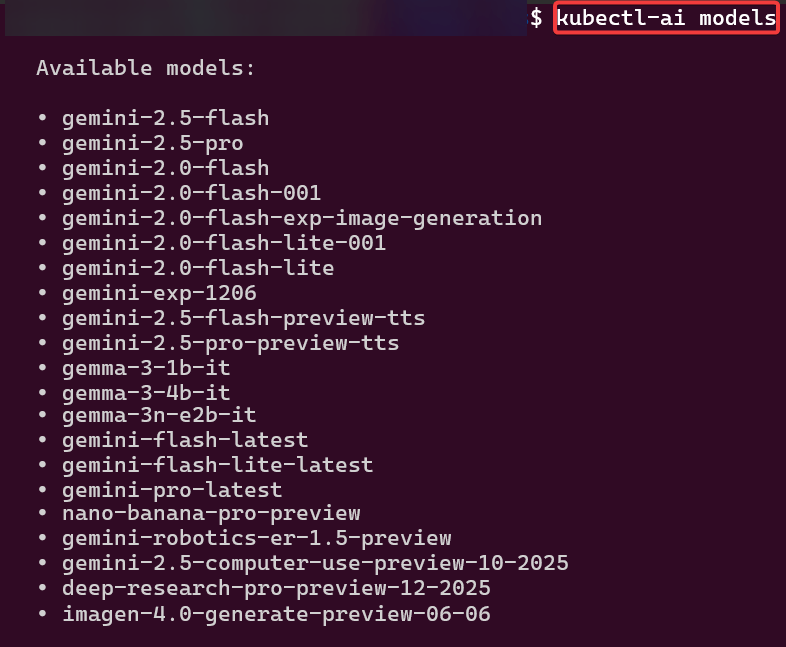
Example 1:
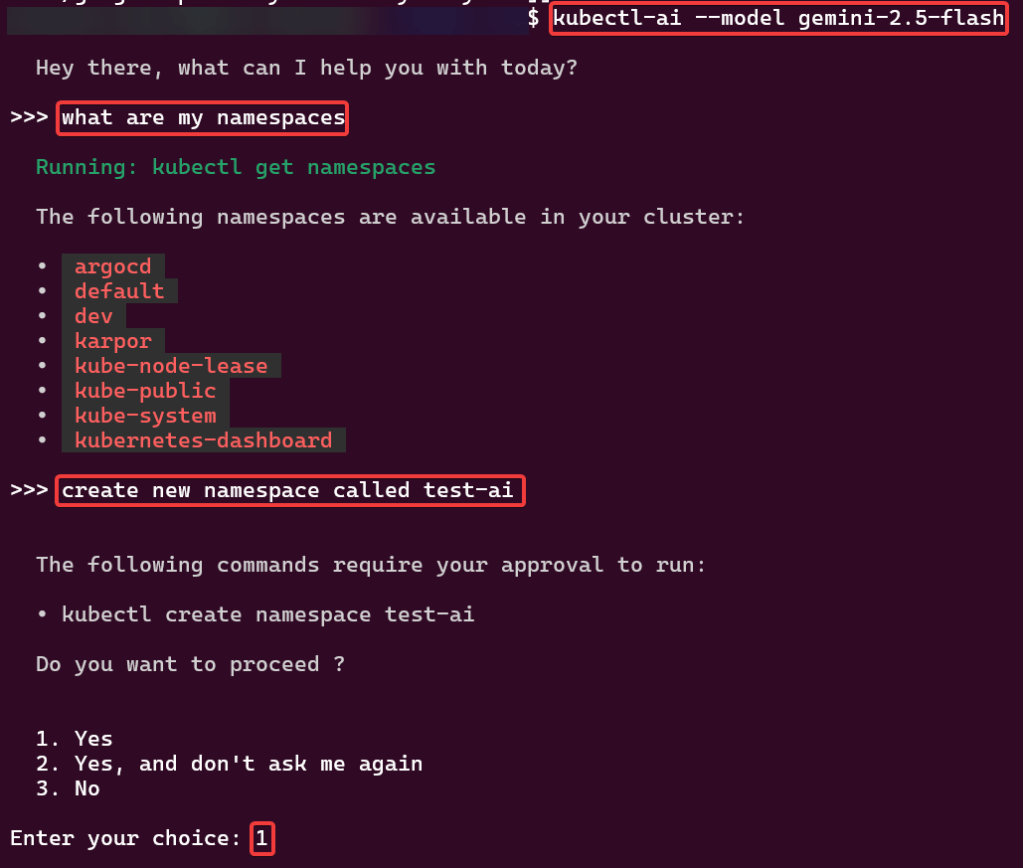
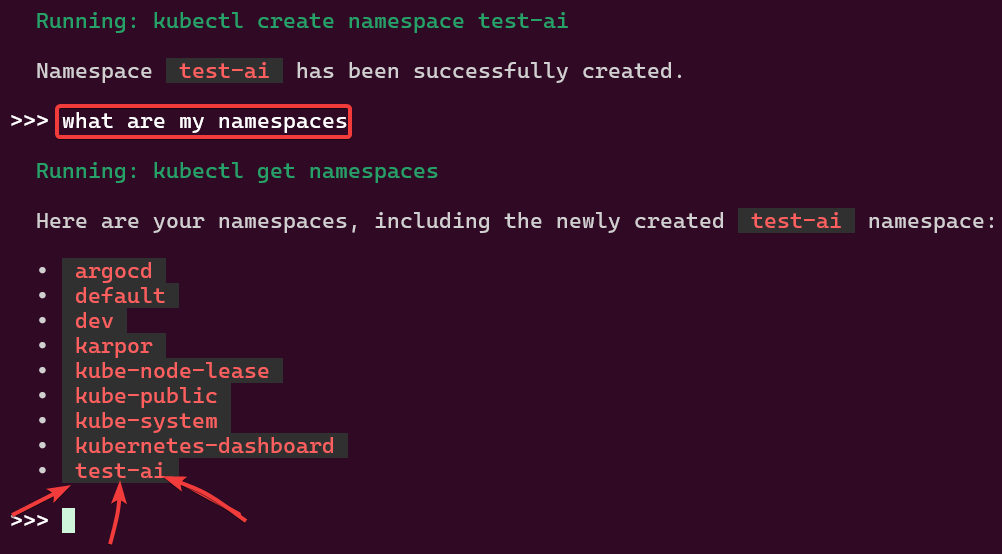
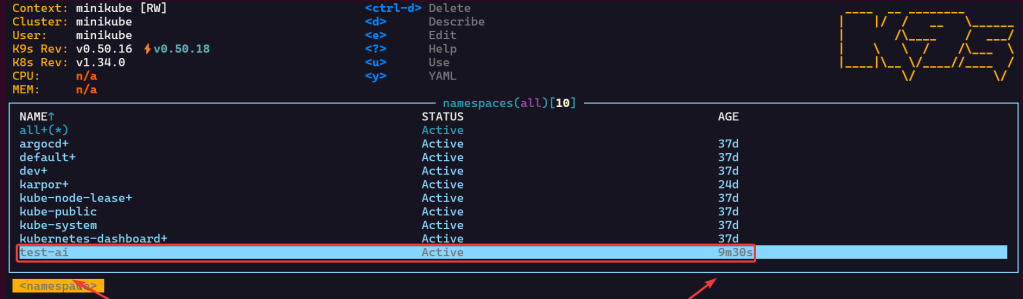
Example 2:
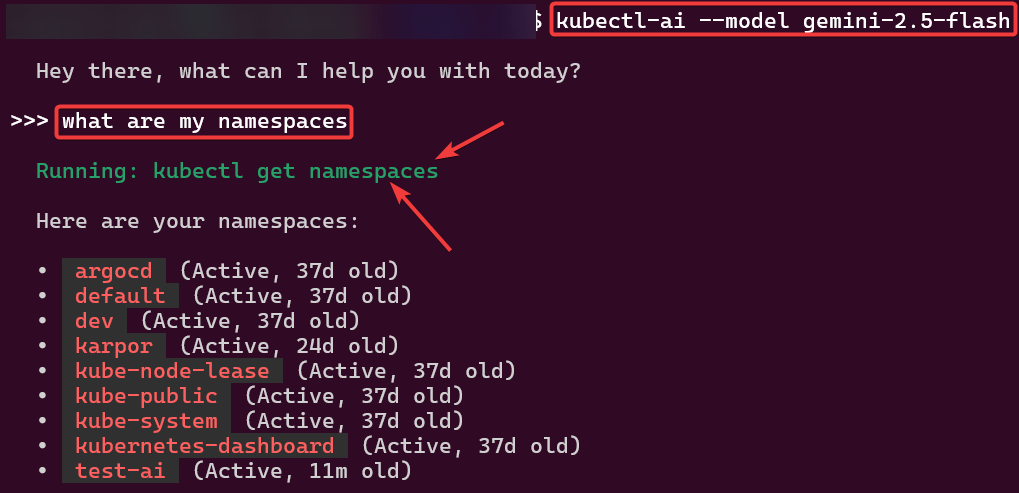
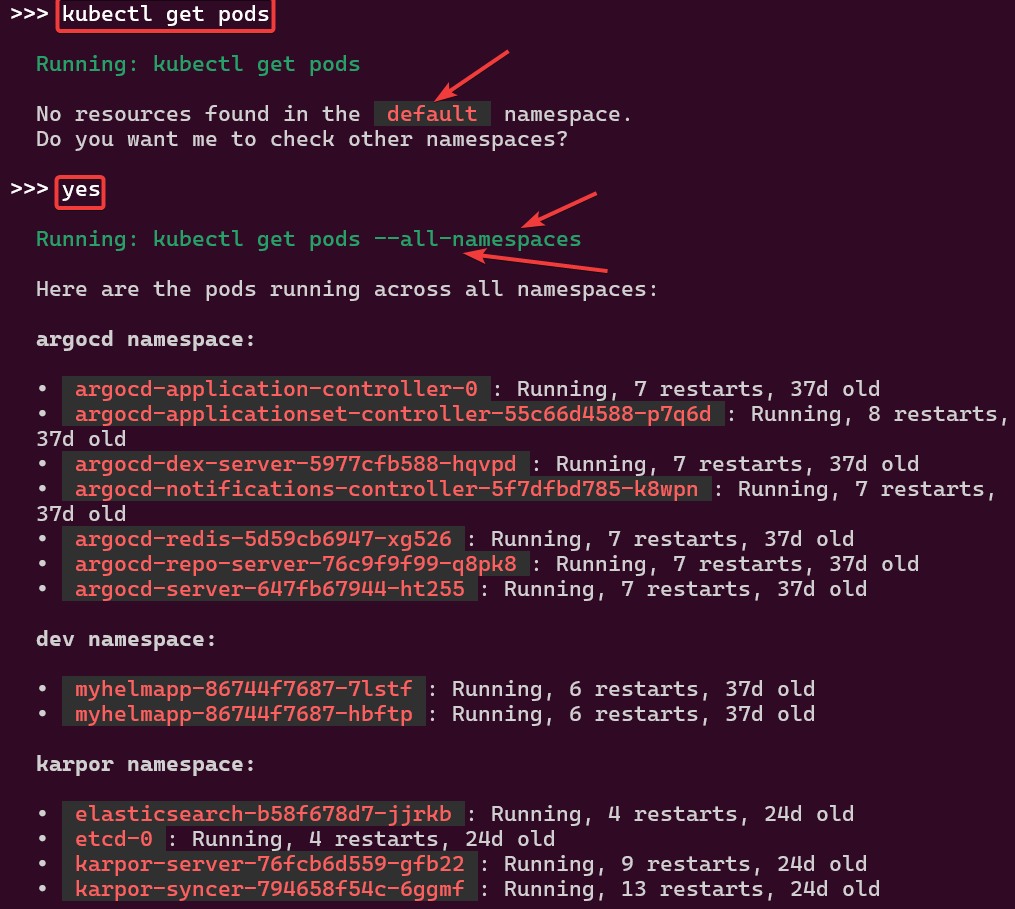
Example 3:
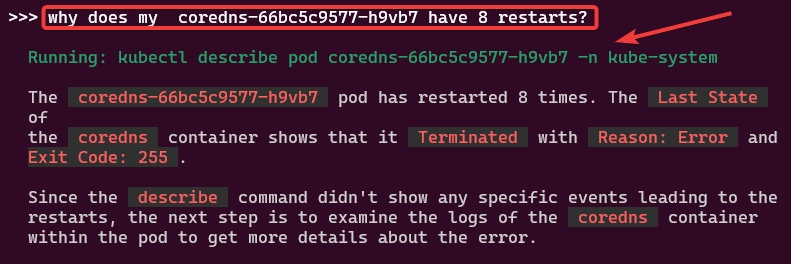
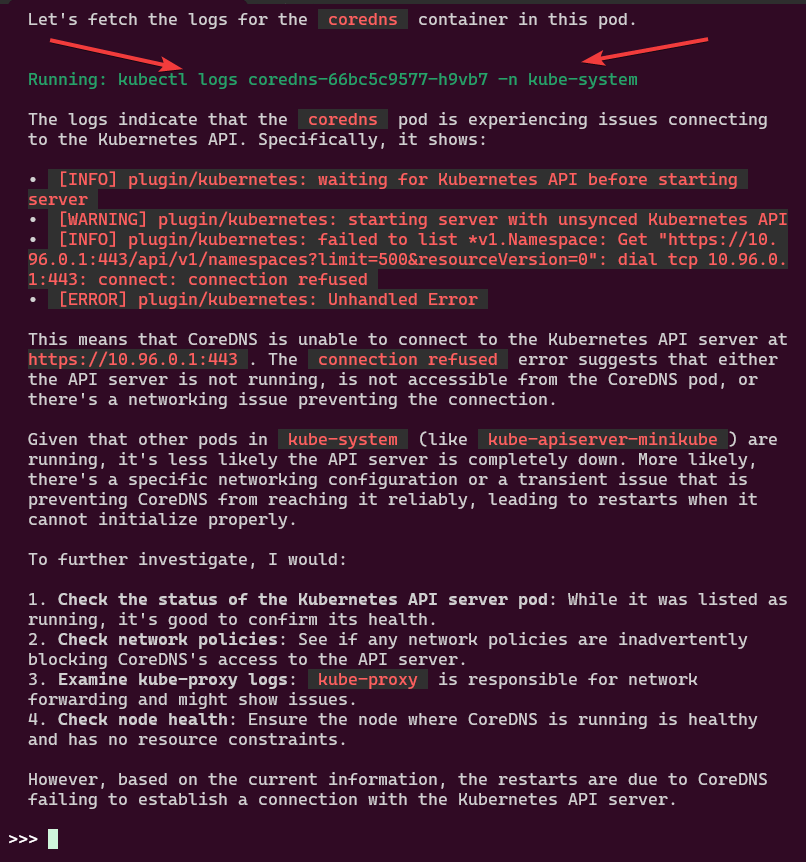
Example 4:
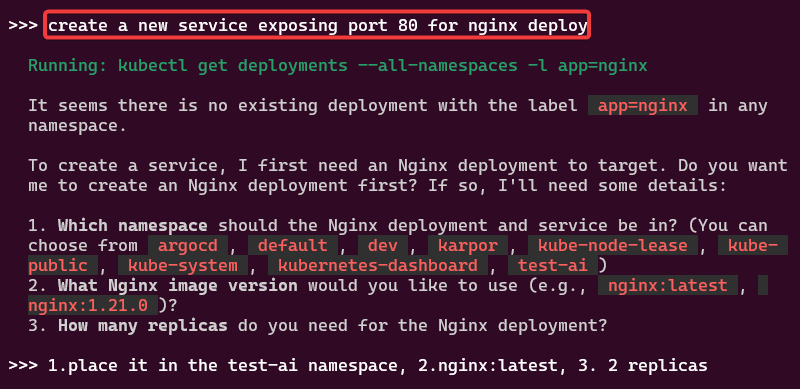
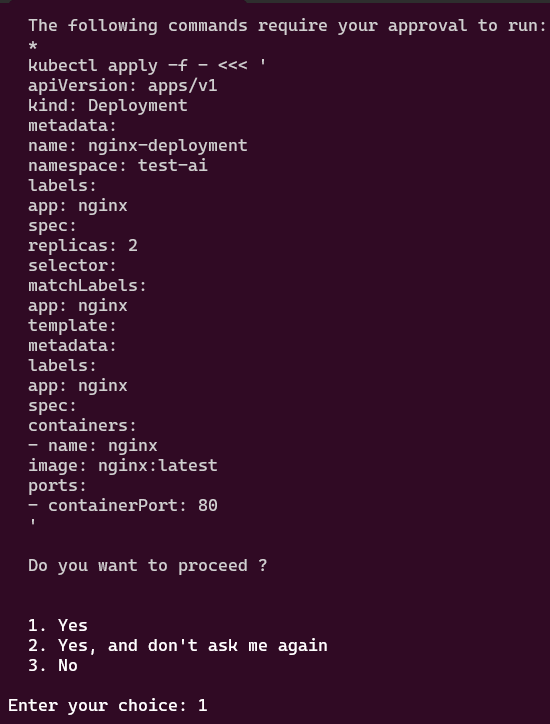
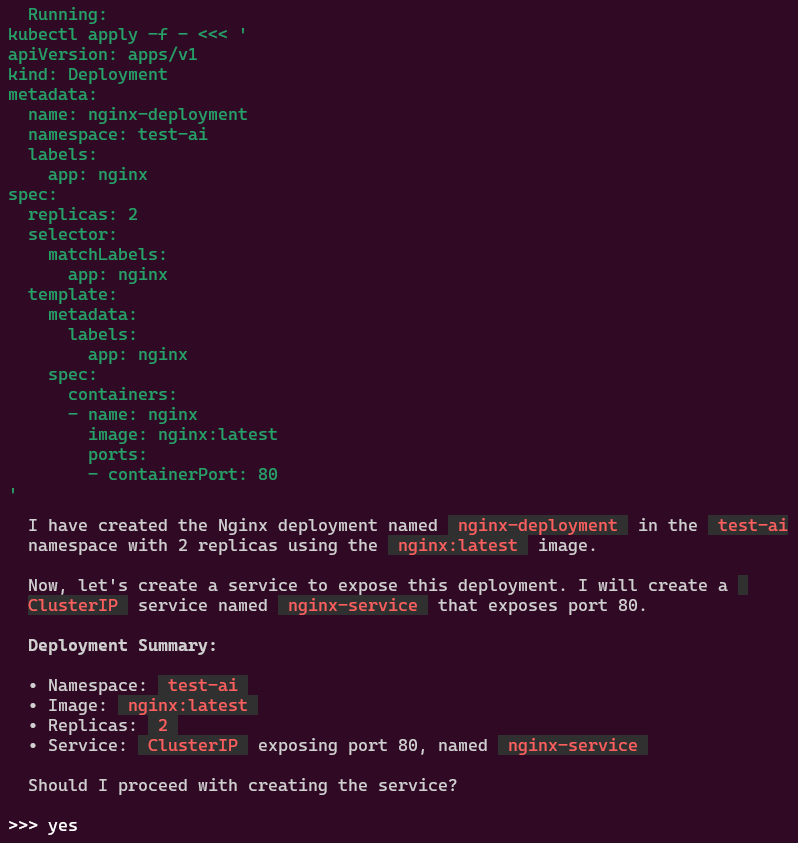
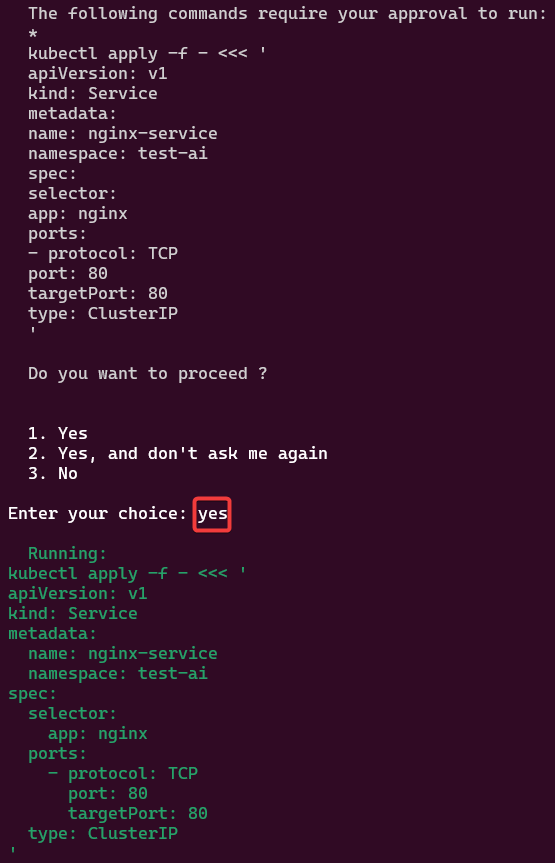

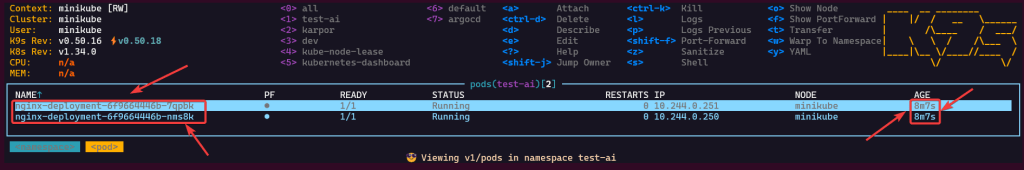
alrite peace


Summary of Steps Below:
git initgit remote add origin https://github.com/<YOUR_GIT_HUB_ACCOUNT>/my-app.gitgit add .git commit -m "terraform code update for my app"git push --set-upstream origin master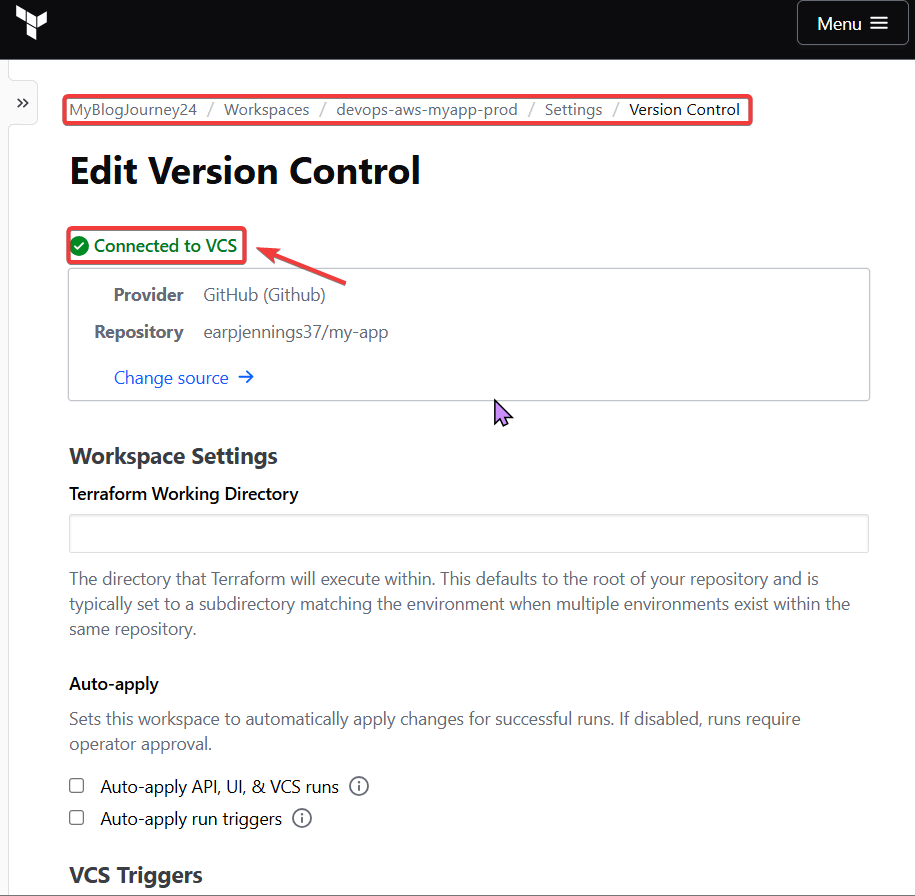
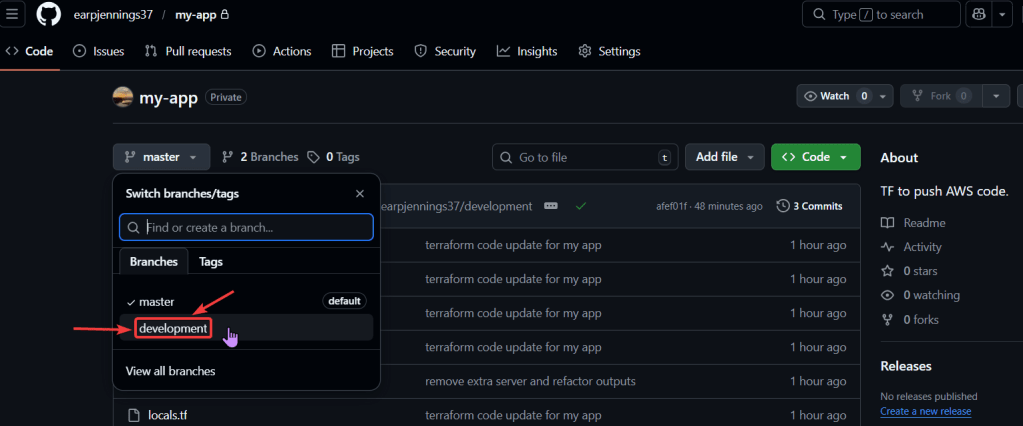
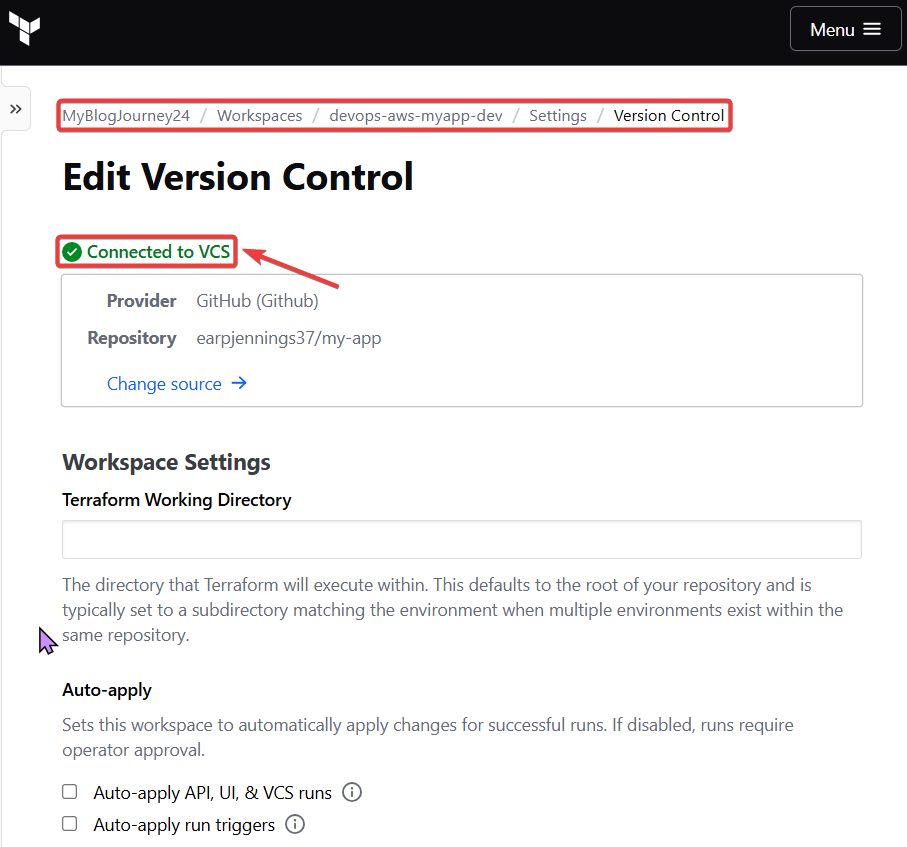
git branch -f development origin/developmentgit checkout developmentgit branchterraform init -backend-config=dev.hcl -reconfigureterraform validateterraform plan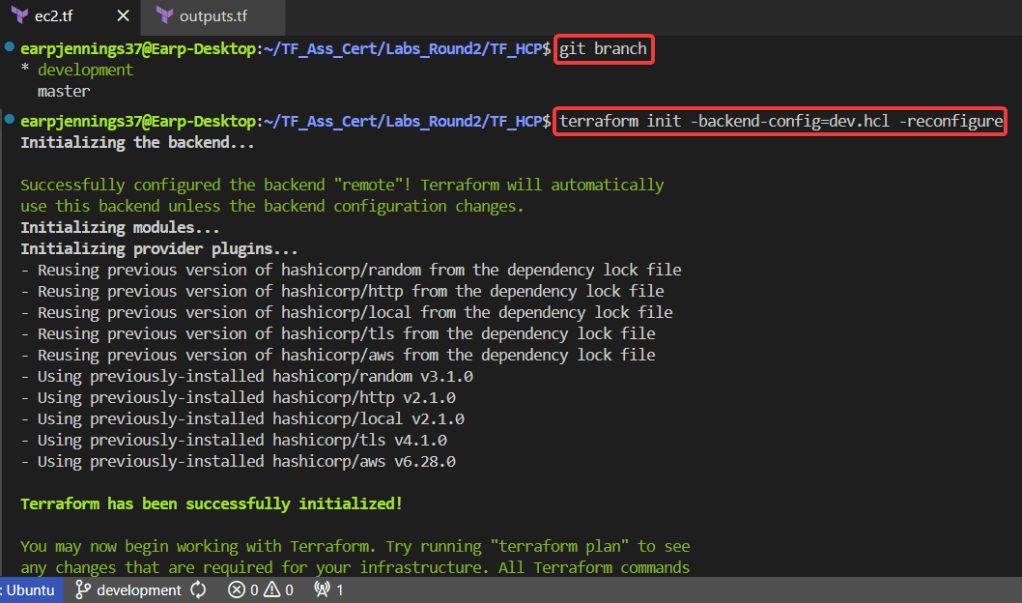
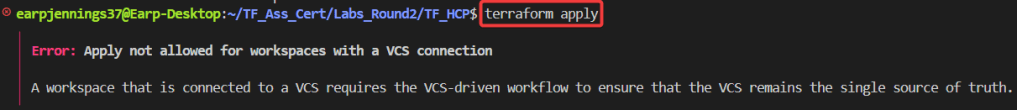
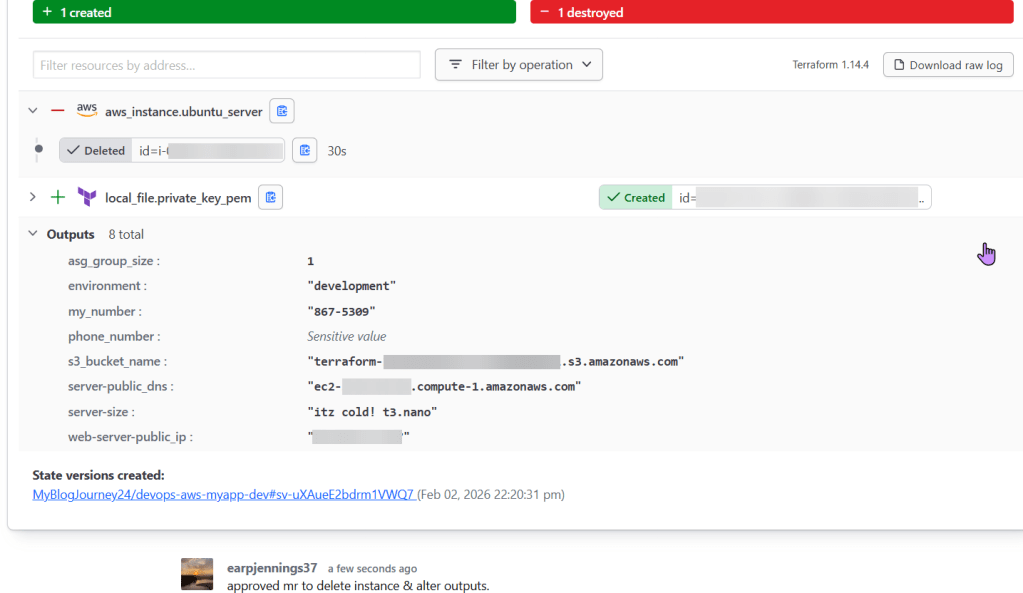
git statusgit add .git commit -m "remove extra server & refactor outputs"git push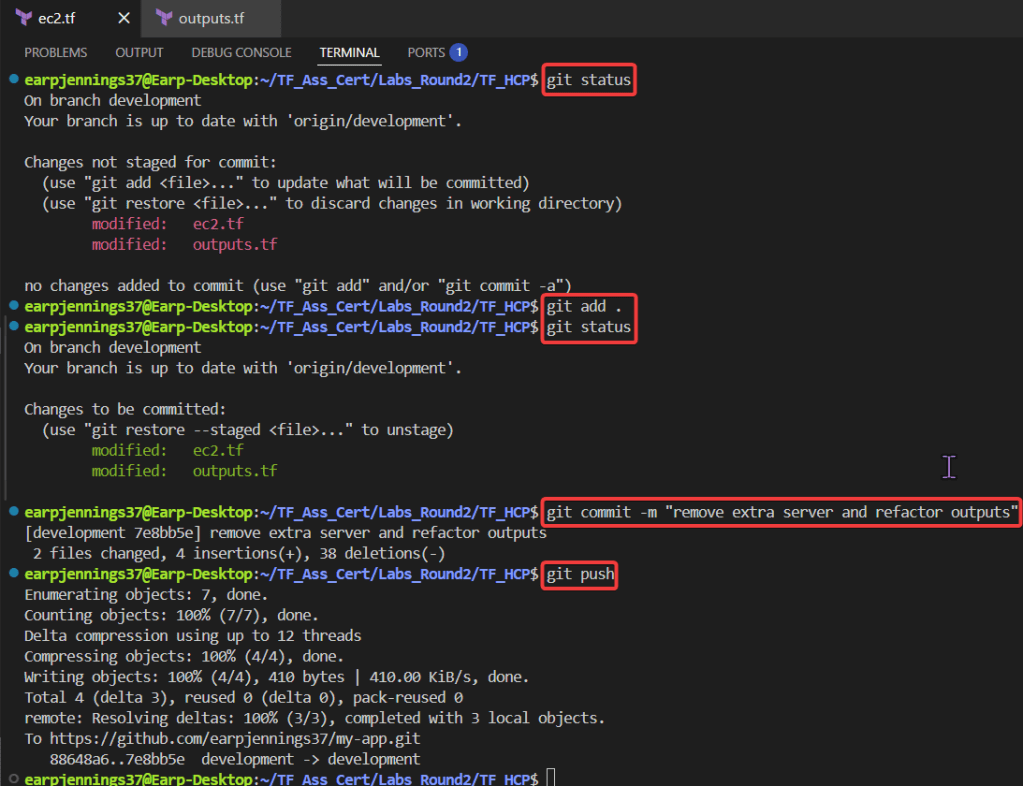
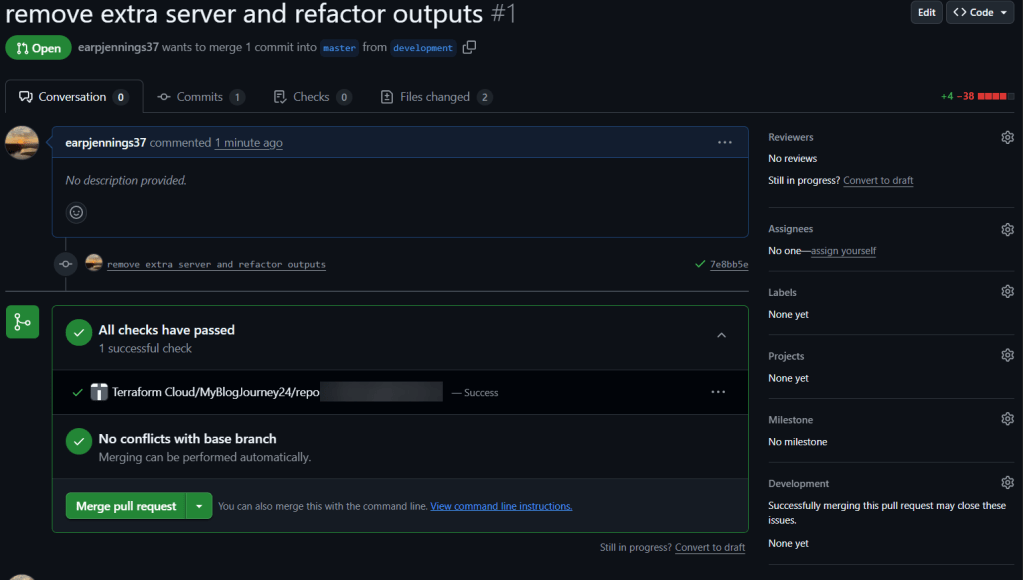
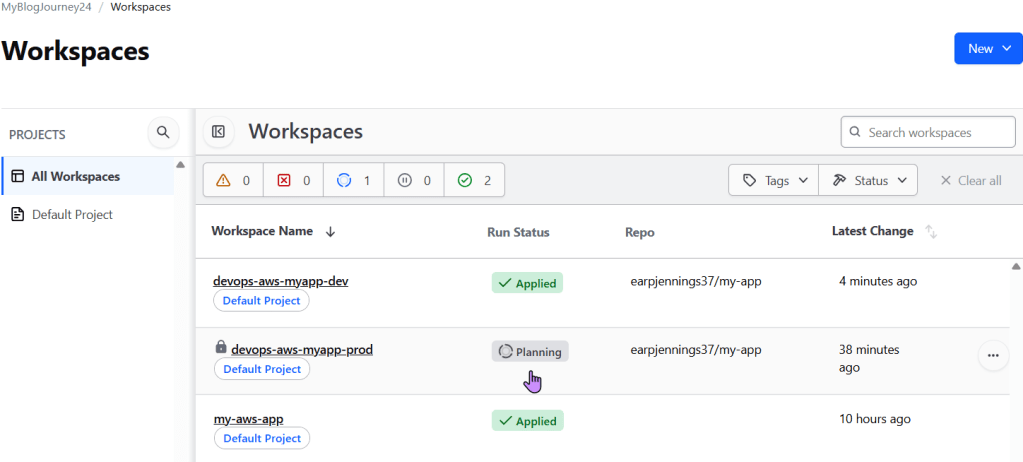
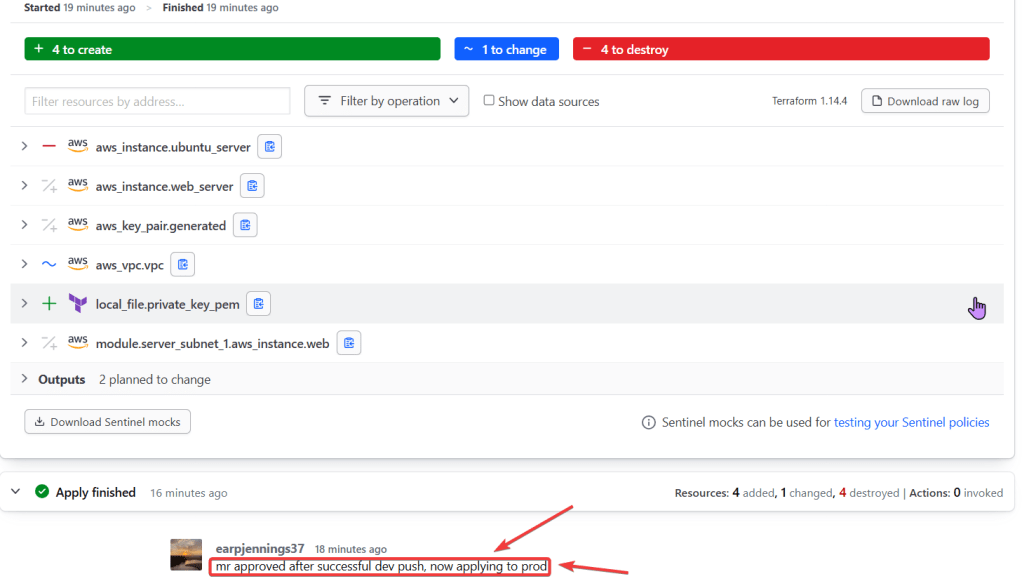
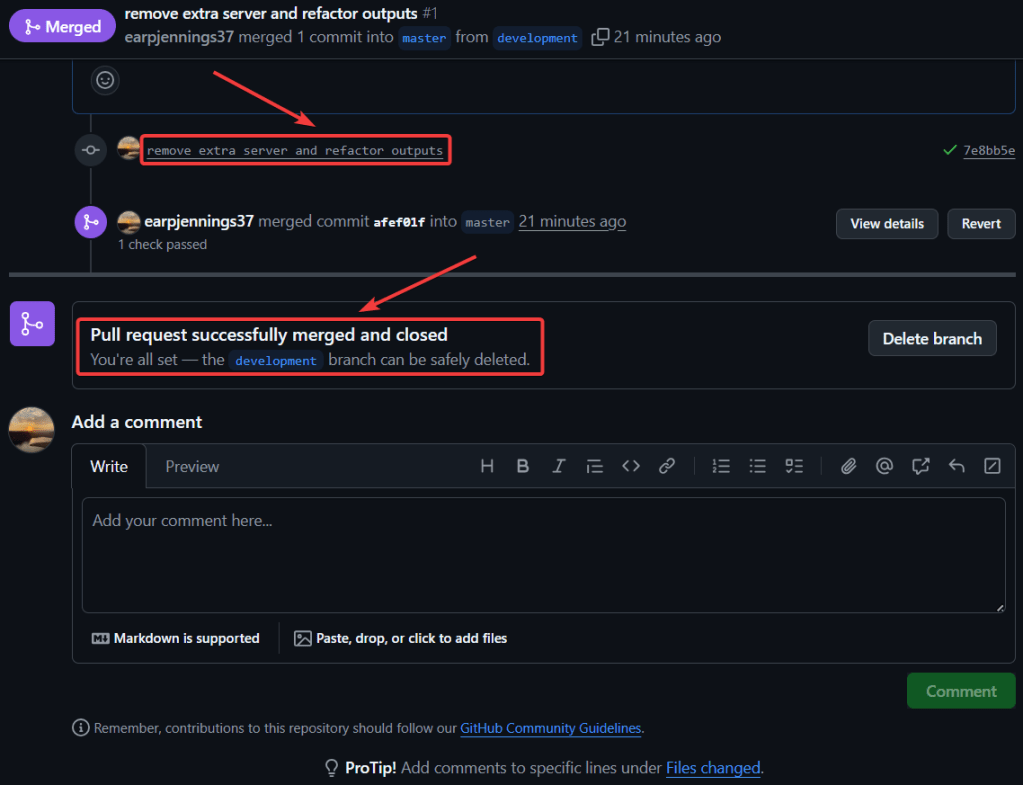

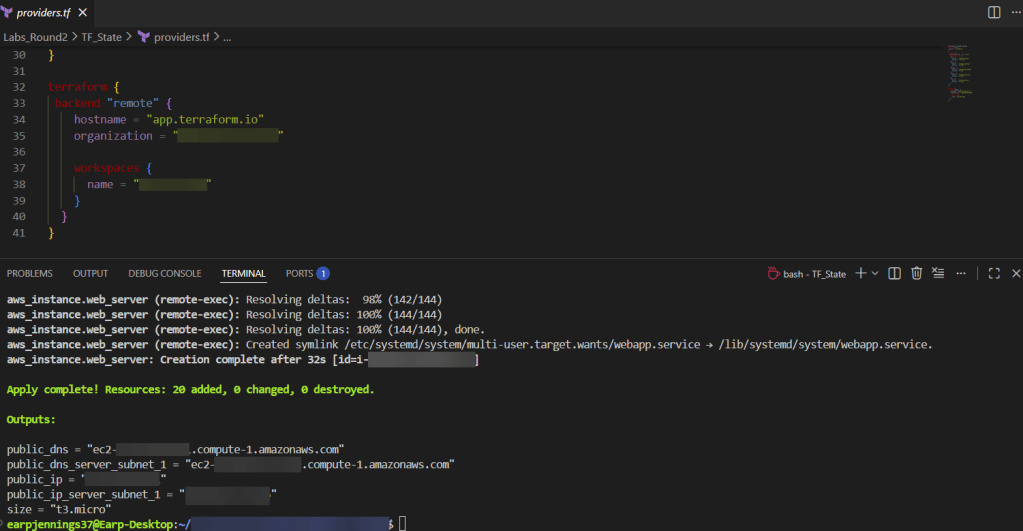
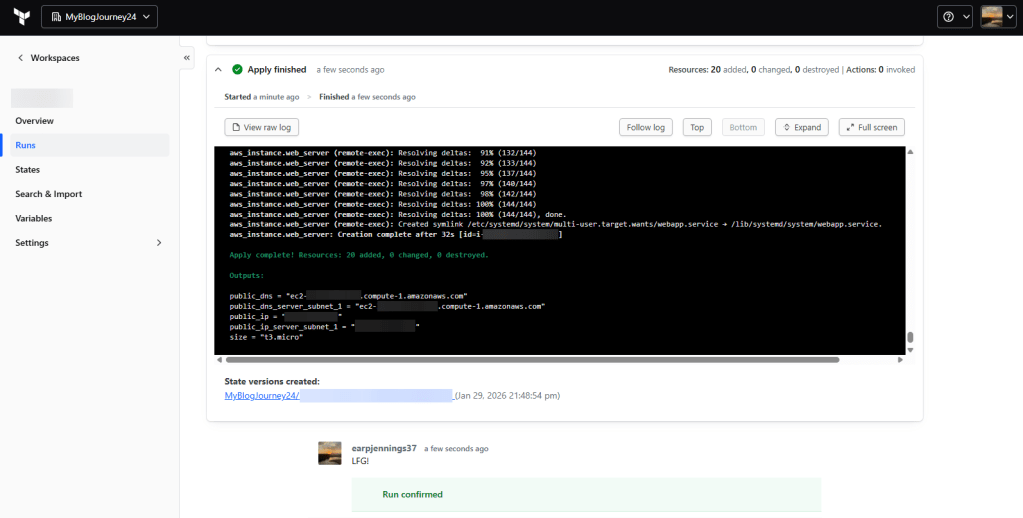
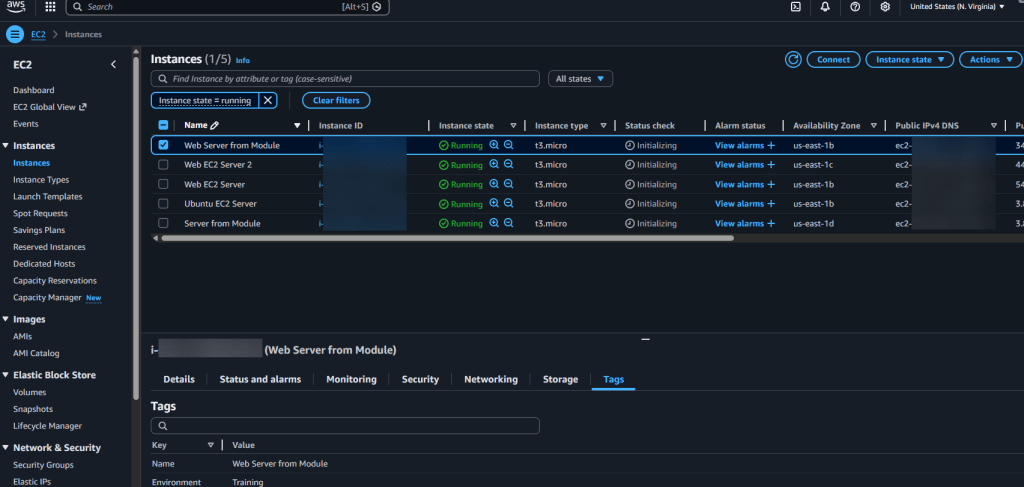
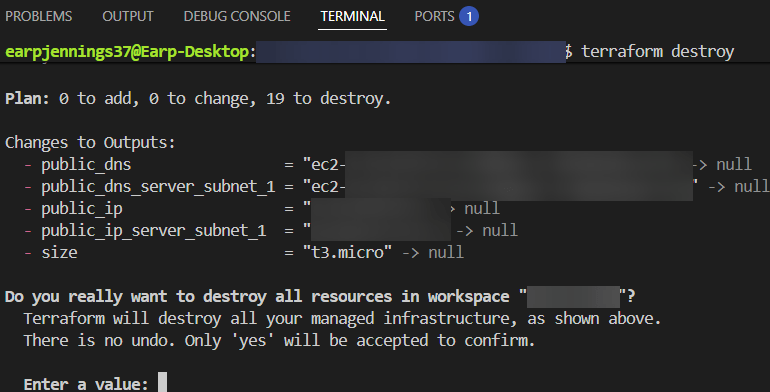
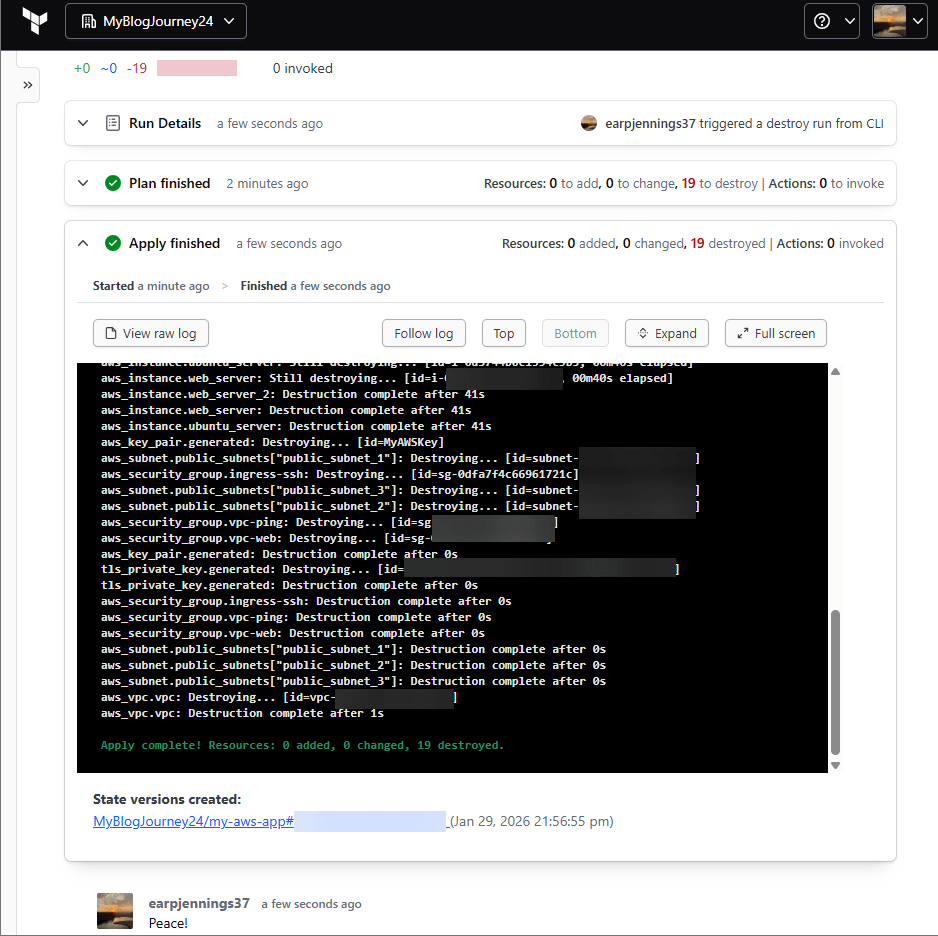

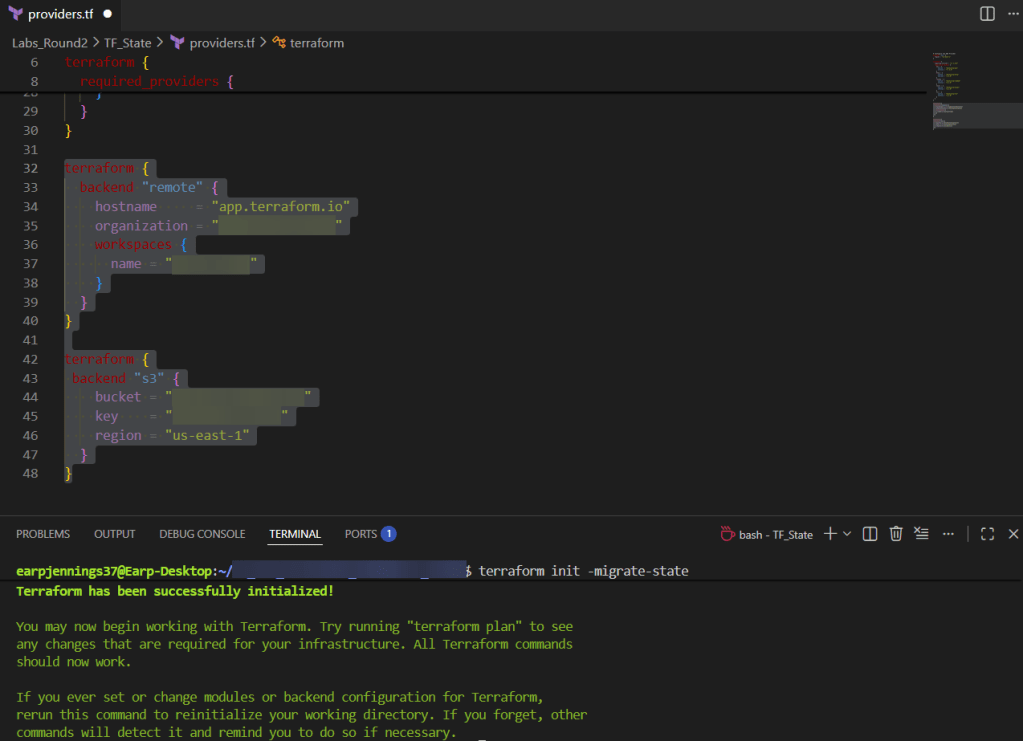

.TF Files:
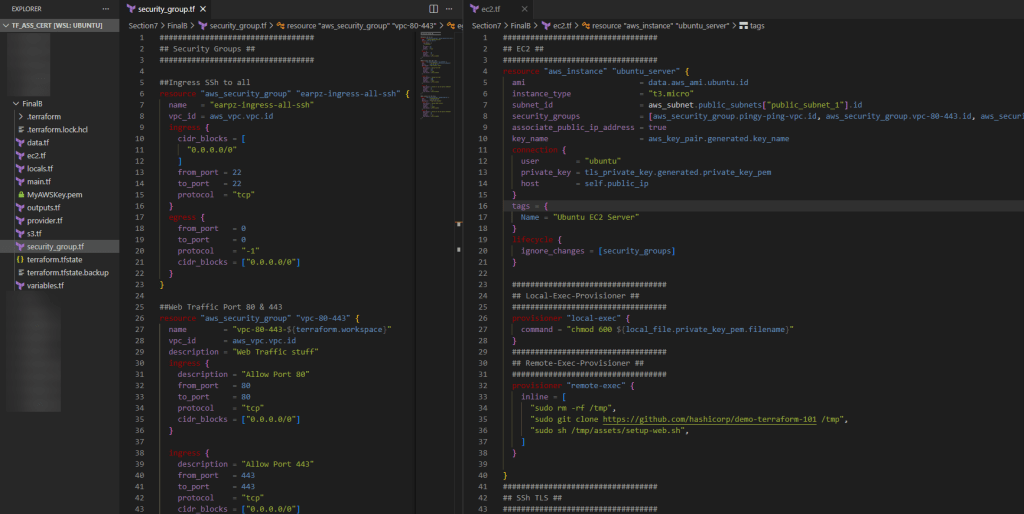
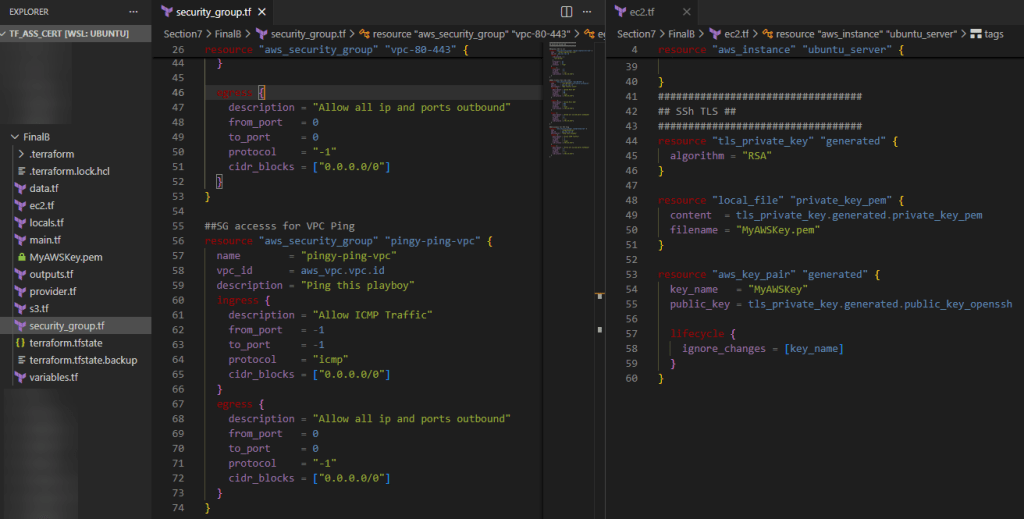
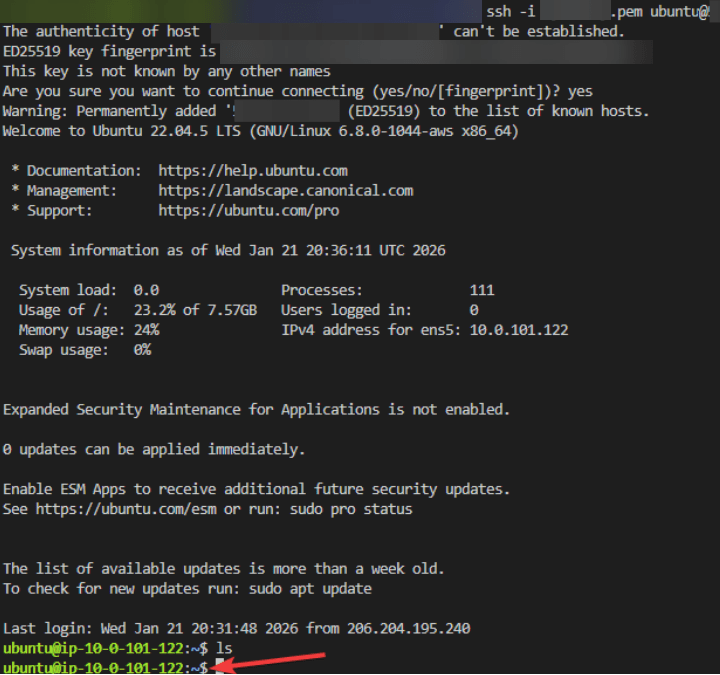
CLI:
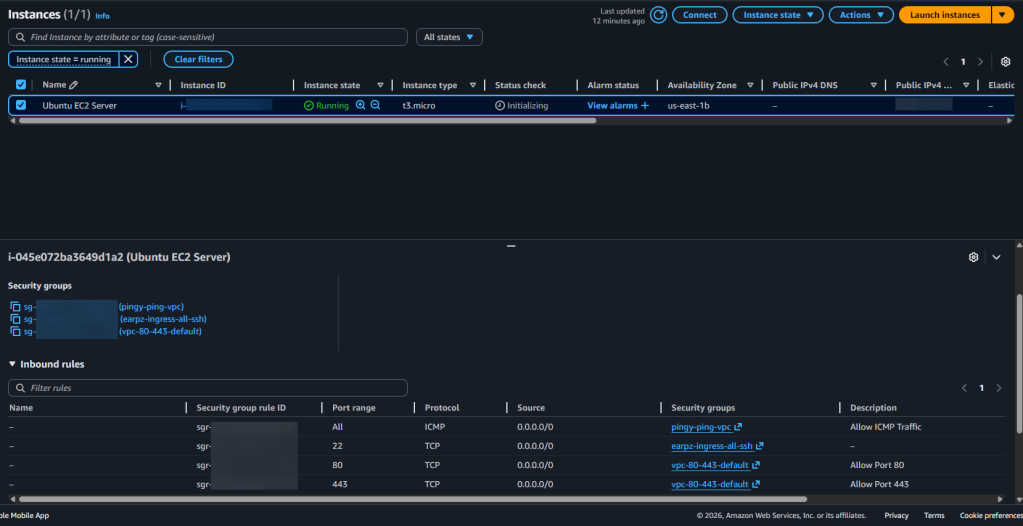
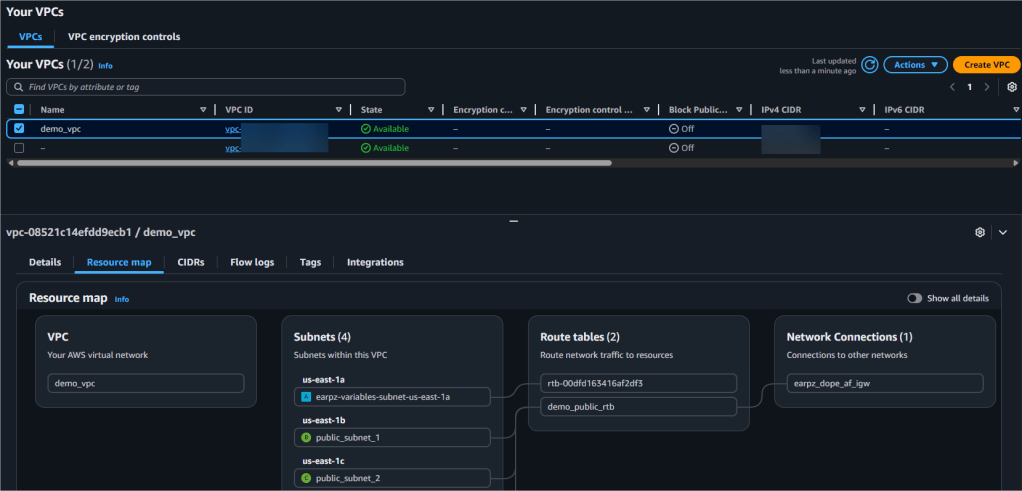
AWS:
Web-Server Public IP Address:

Install KusionStack Karpor CLI:
# brew tap KusionStack/tap# brew install KusionStack/tap/kusionHelm Repo Add Karpor
# helm repo add kusionstack https://kusionstack.github.io/charts# helm repo update# helm install karpor kusionstack/karpor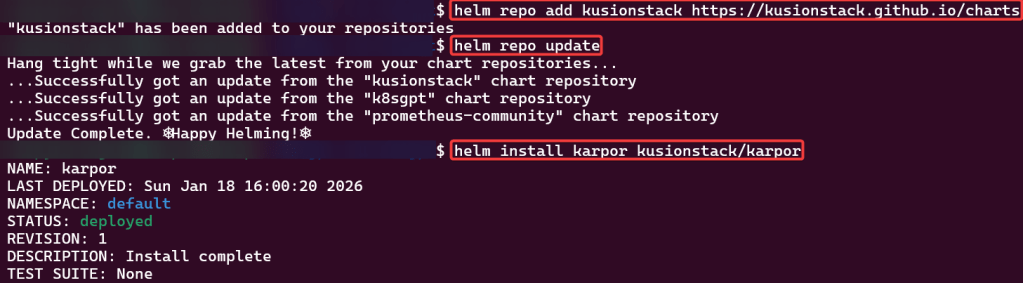
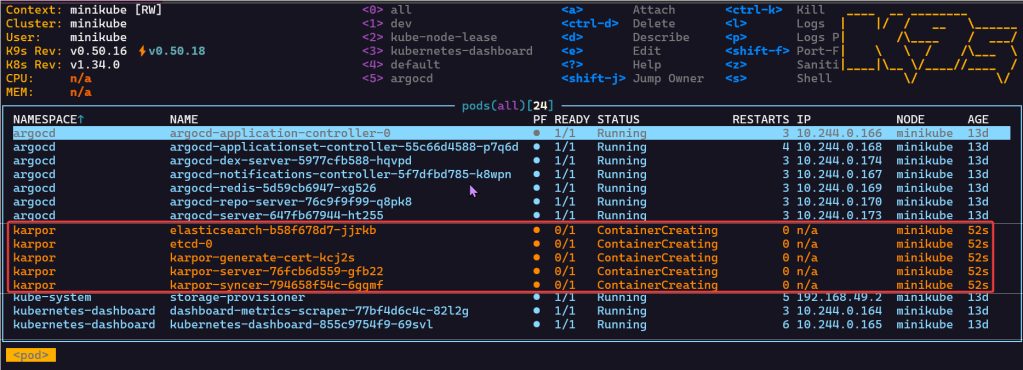
Port-Forward to 7443 & Review Dashboard:


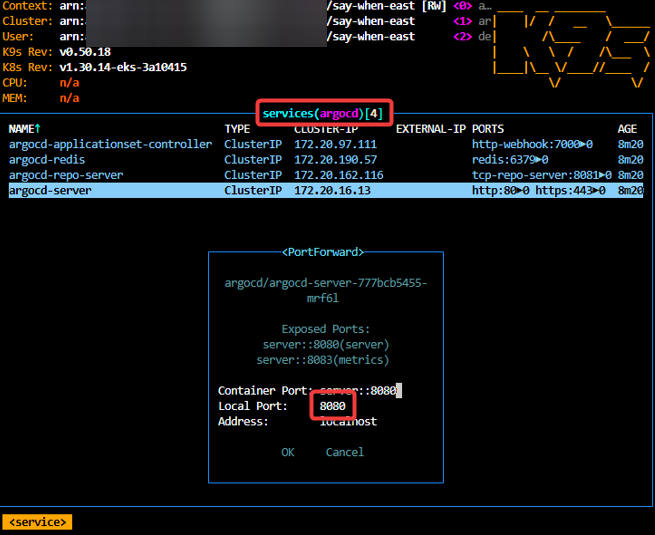
Install ArgoCD:
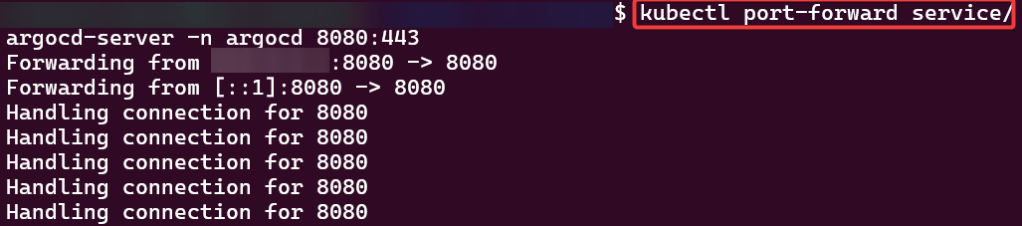
brew install argocdkubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8080:443argocd login 127.0.0.1:8080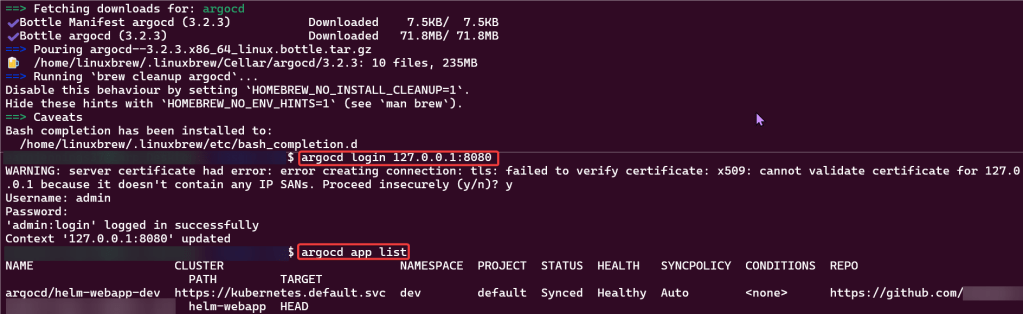

Code:
kubectl create namespace argocdkubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml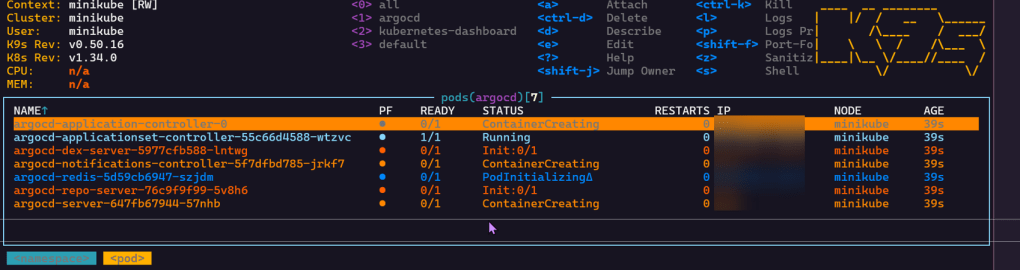
Port-forward:

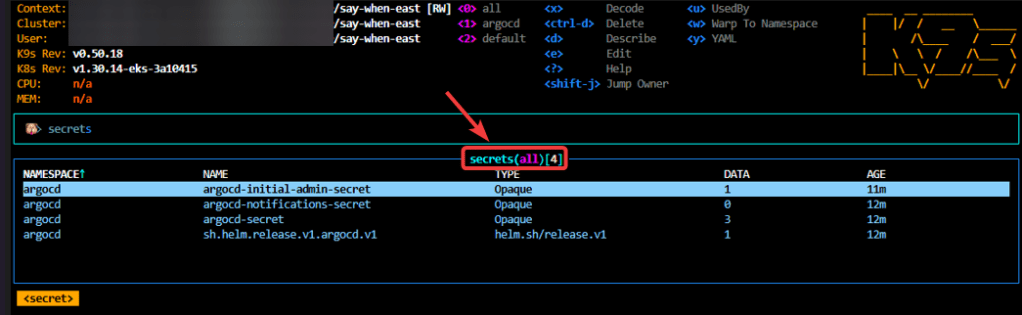
“Secret” Password:
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d
Helm Chart install:
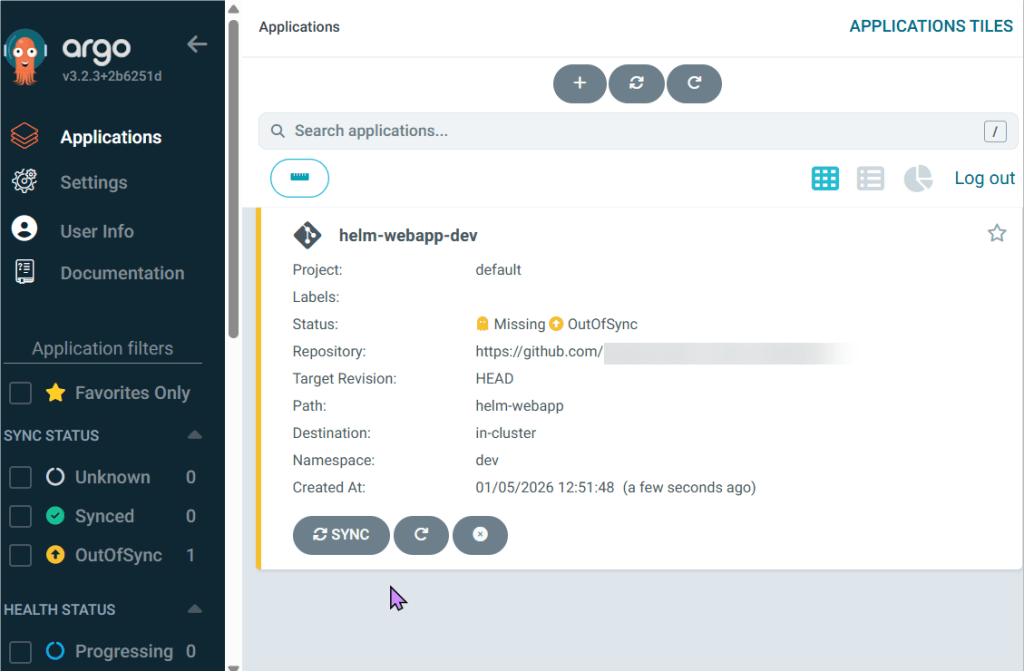

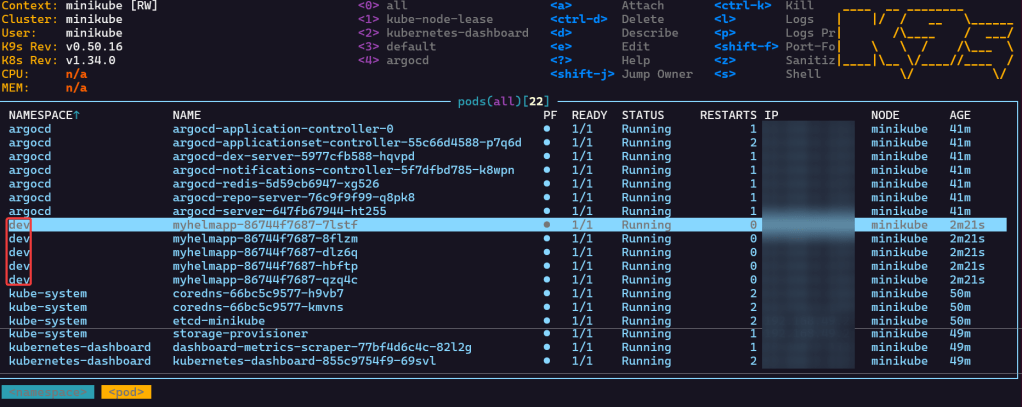


Scale-Up Replicas to 10:
Rollback in ArgoCD