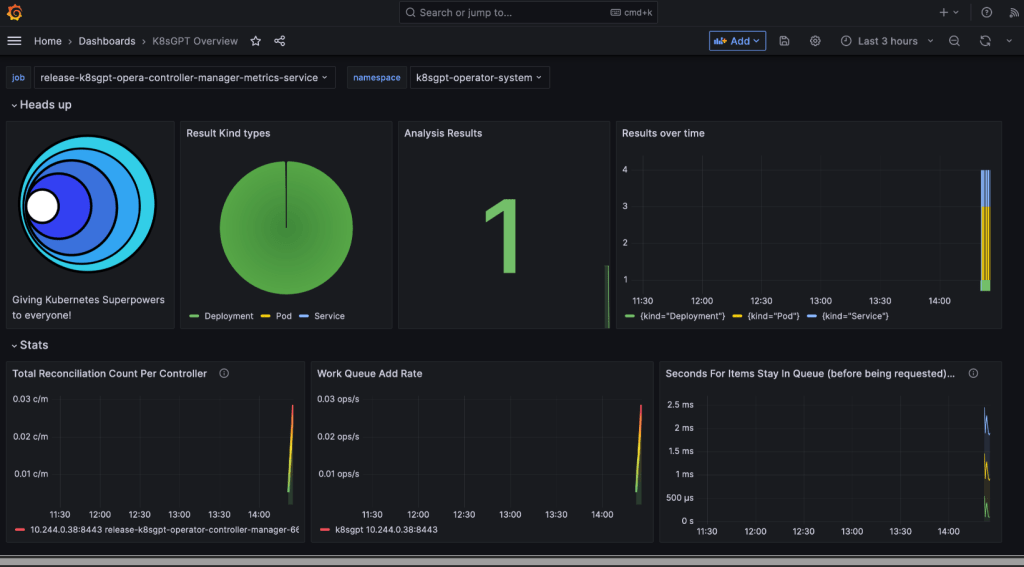
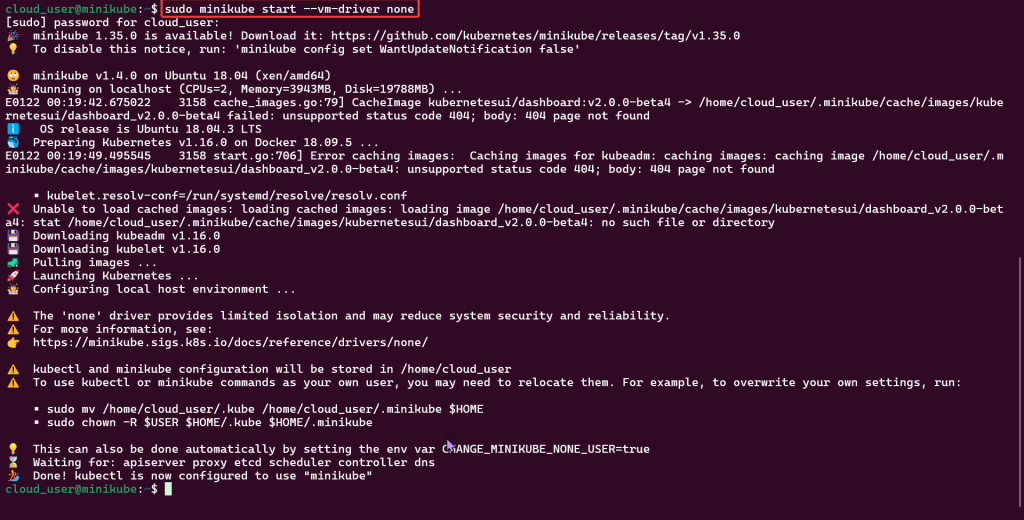
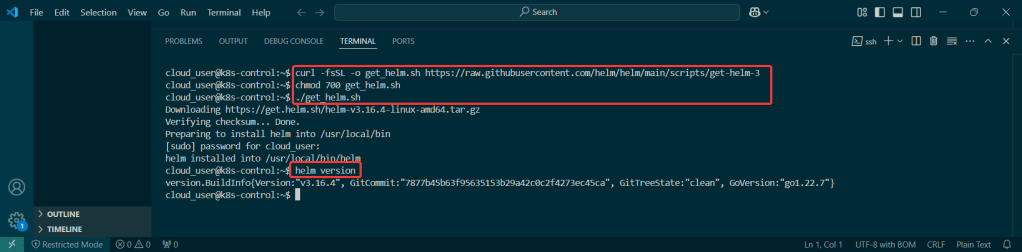
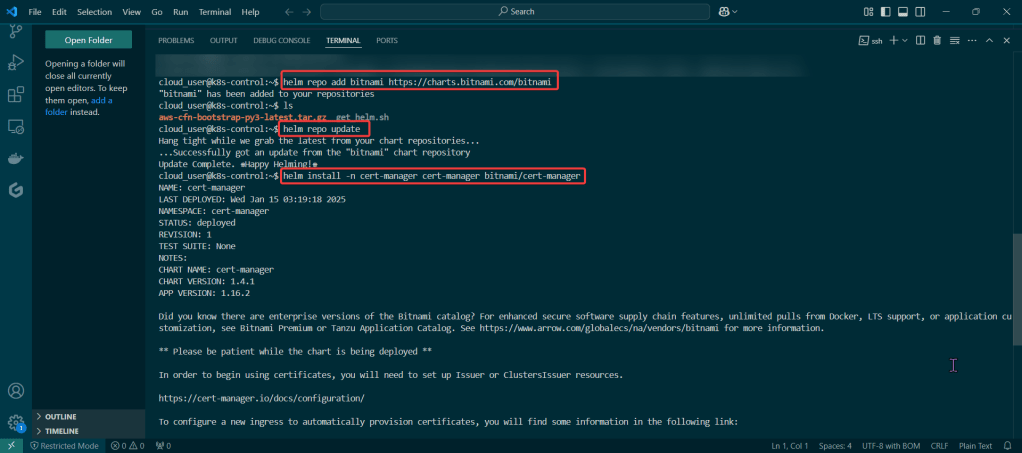
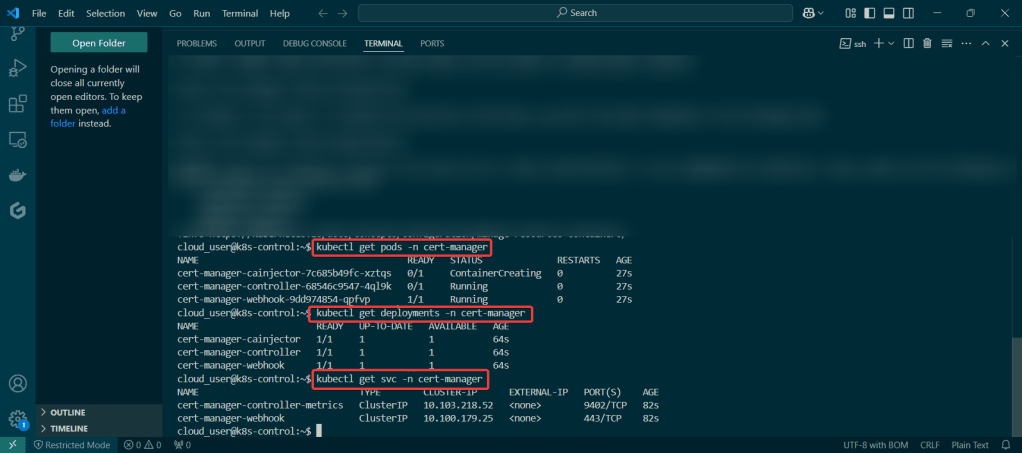
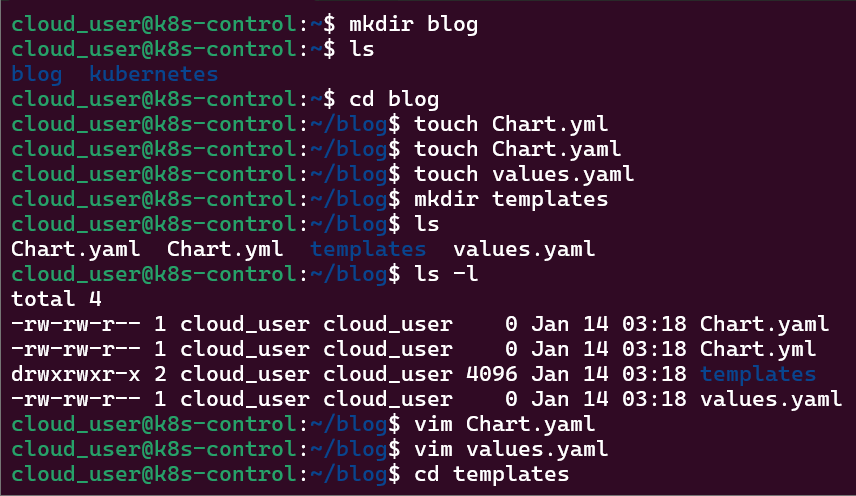
Install ArgoCD:
brew install argocd
kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8080:443
argocd login 127.0.0.1:8080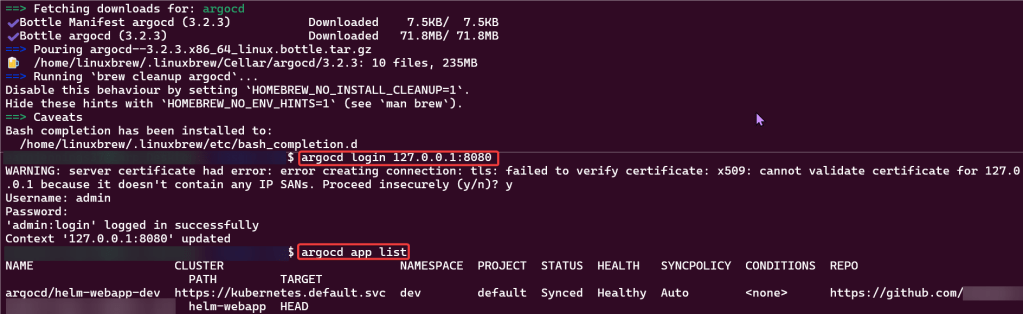

Code:
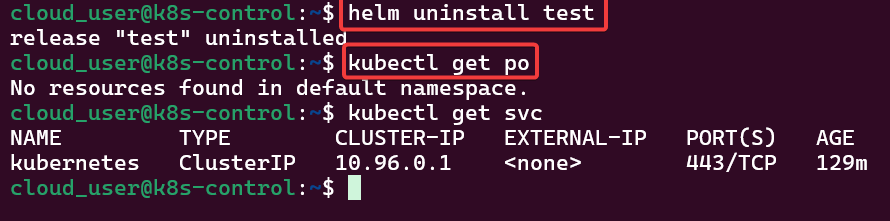
kubectl create namespace argocd
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml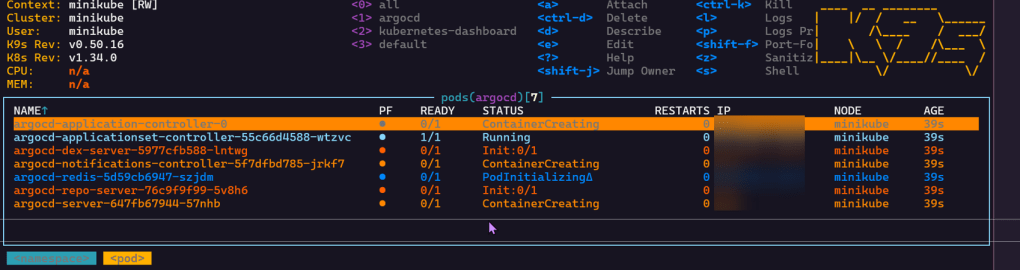
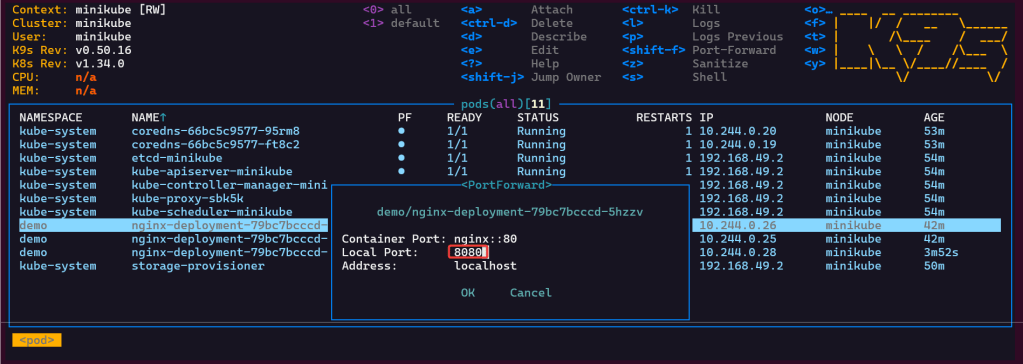
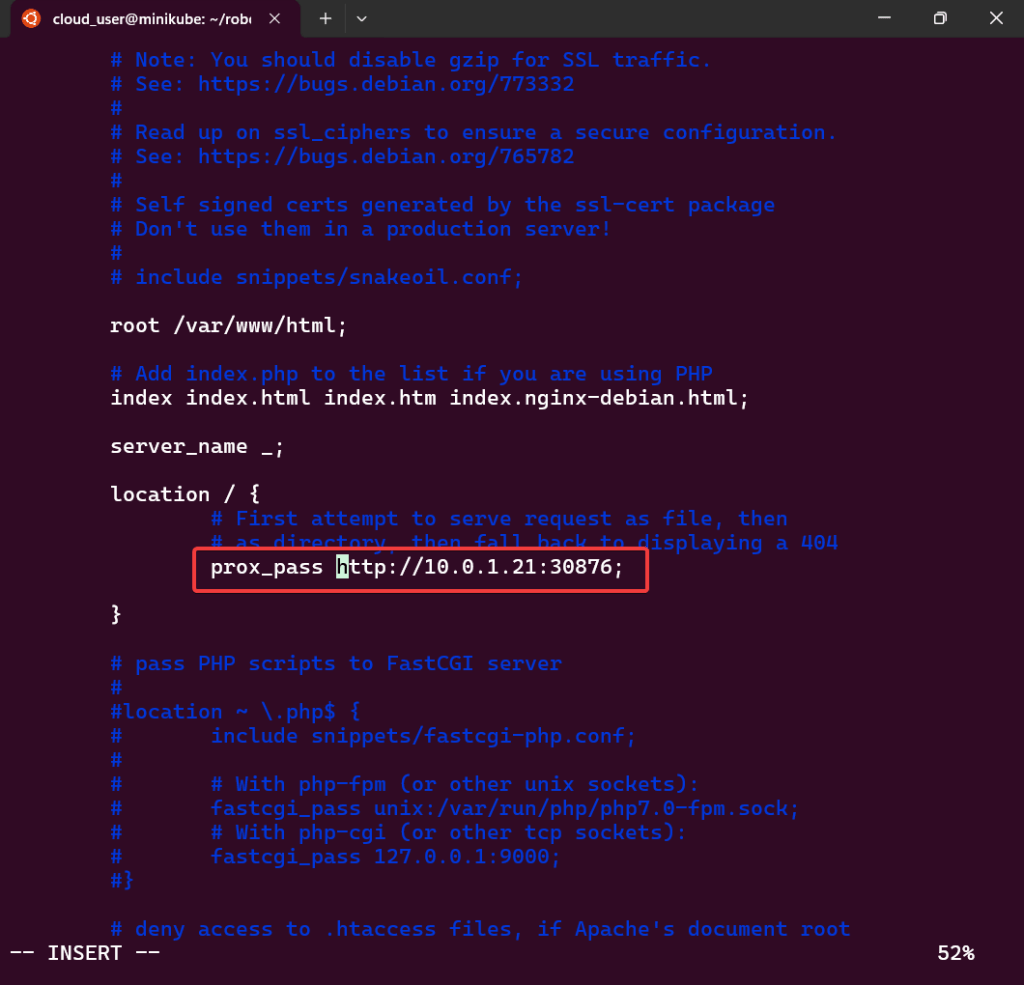
Port-forward:
- Option 1 from CLI
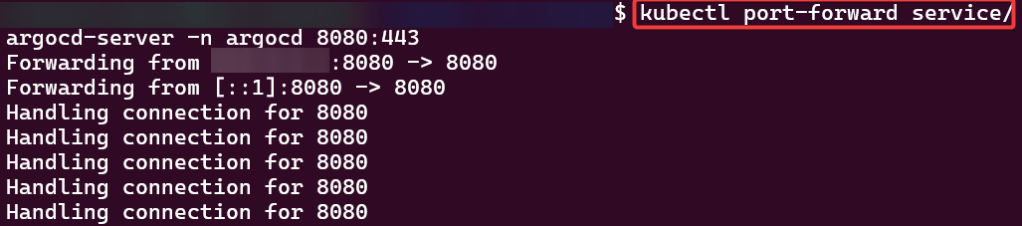
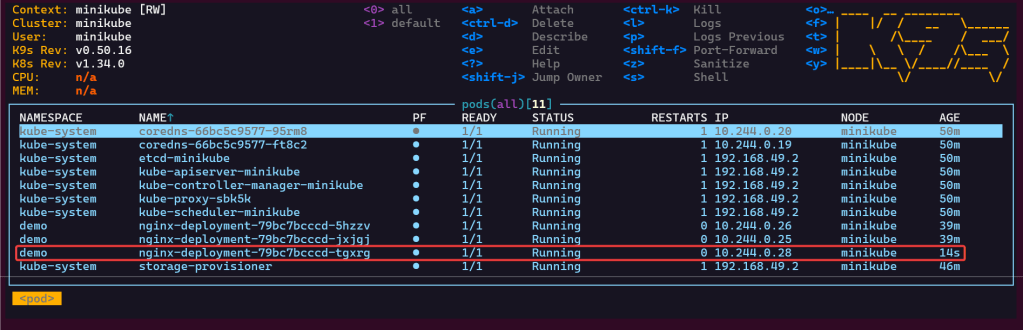
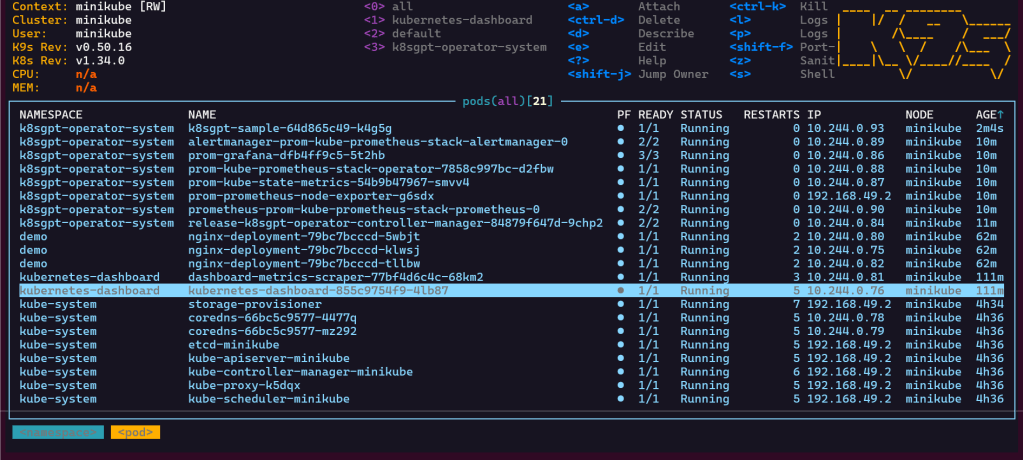
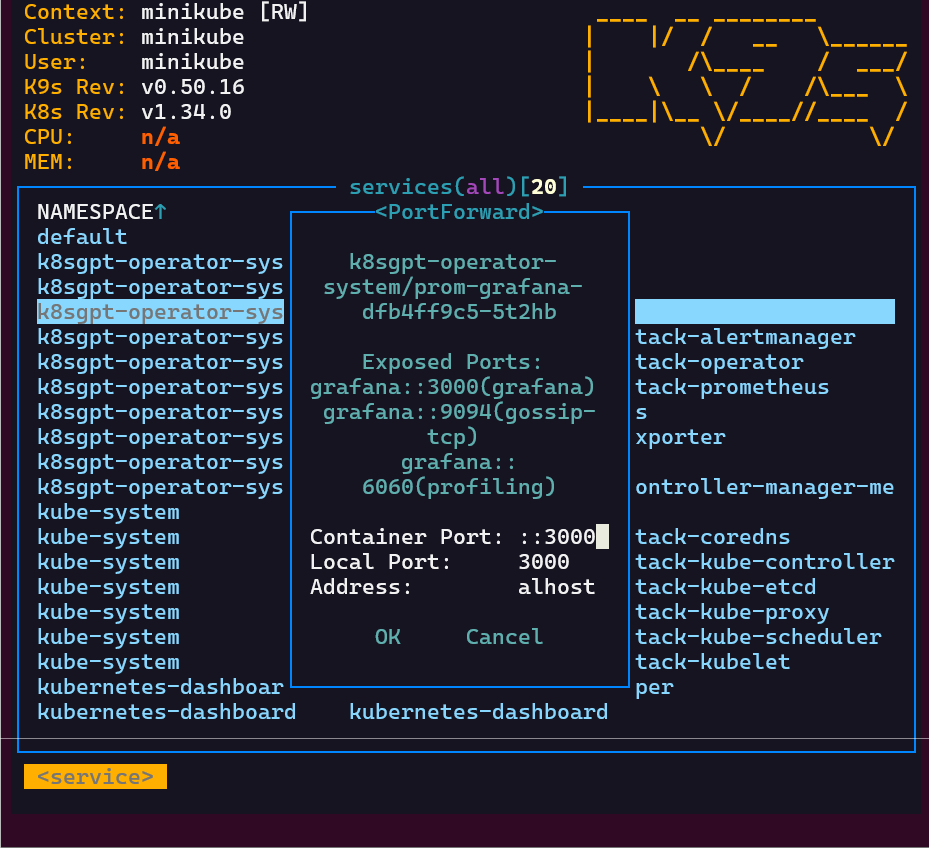
- Option 2 from K9s

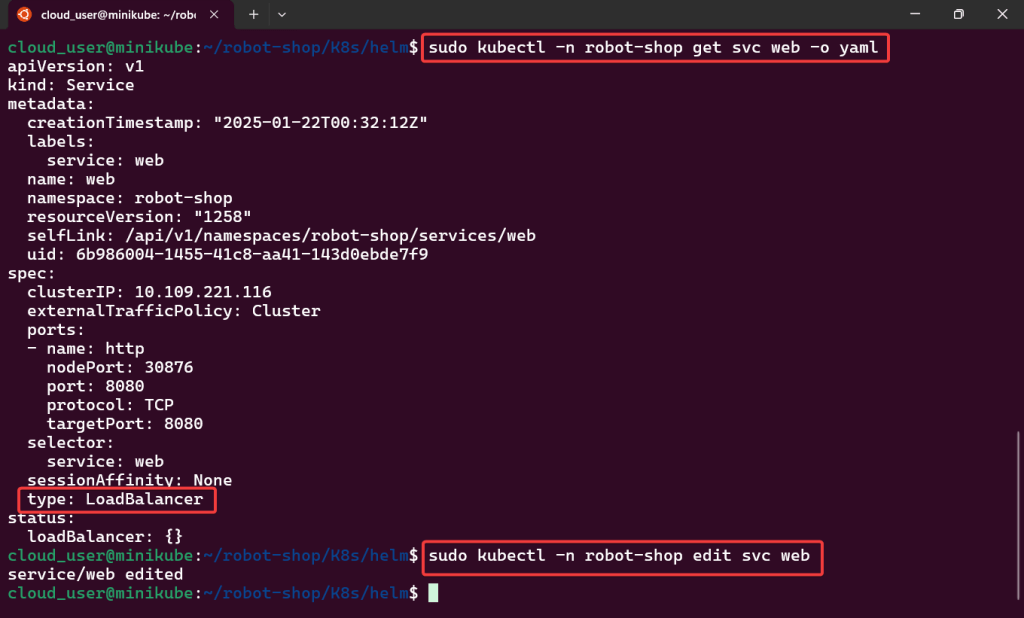
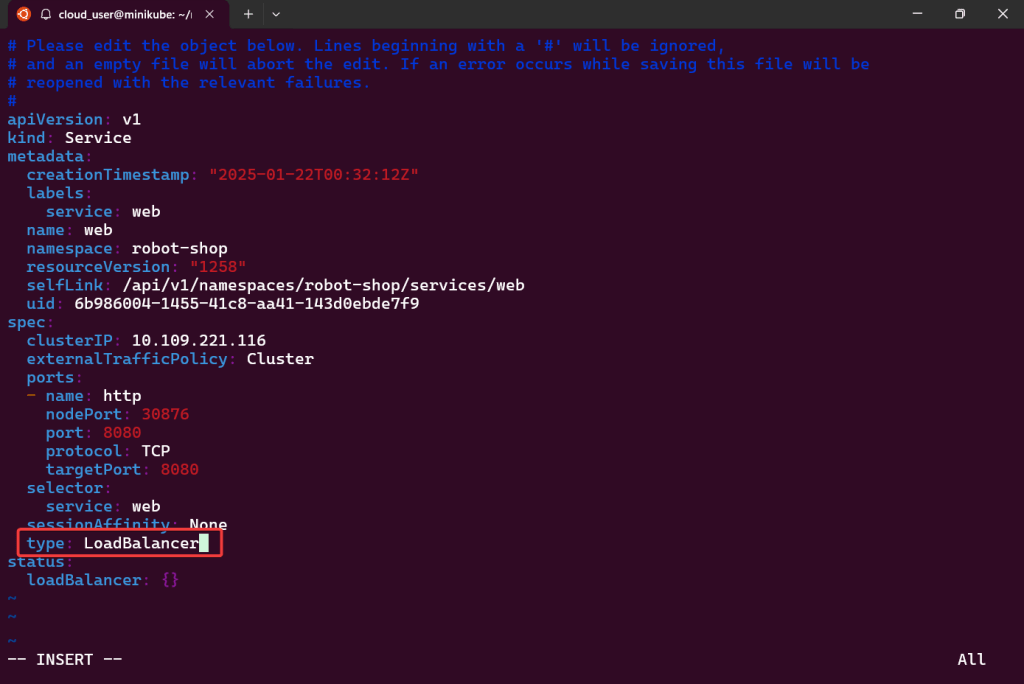
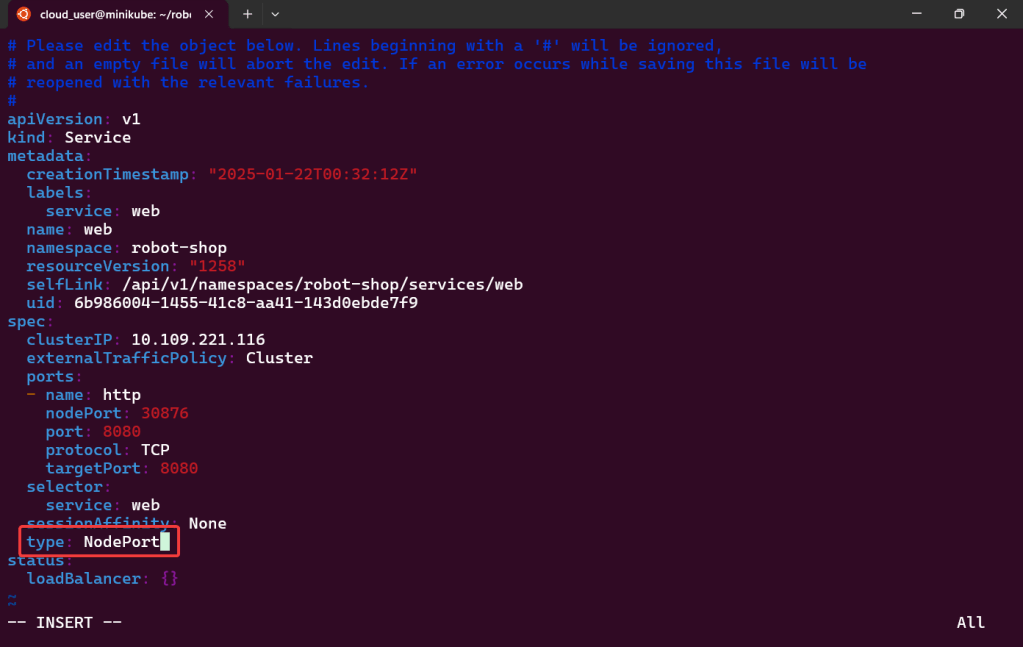
“Secret” Password:
- Option 1 from CLI
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d- Option 2 from K9s
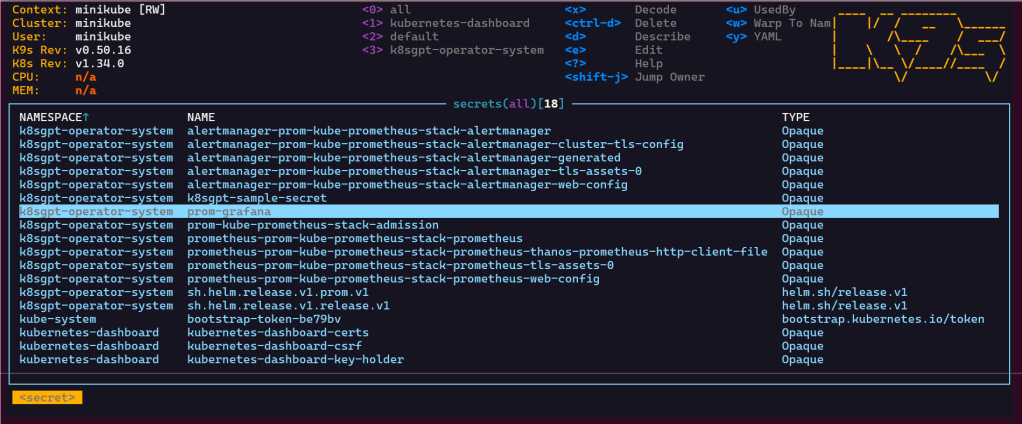
- go to secrets
- hit x on the preferred option you desire
- initial admin secret – login to argocd
- secret – to get RSA private keys

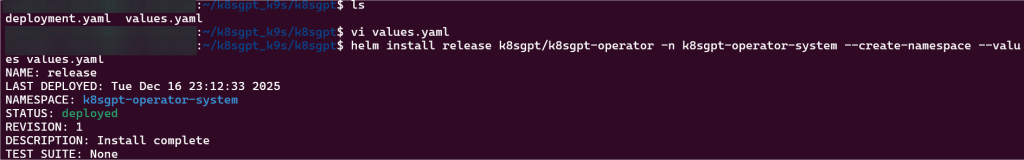
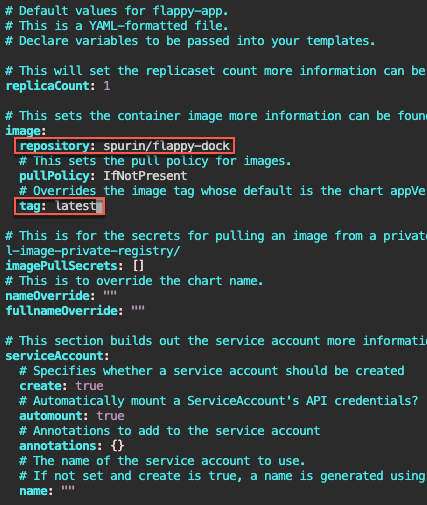
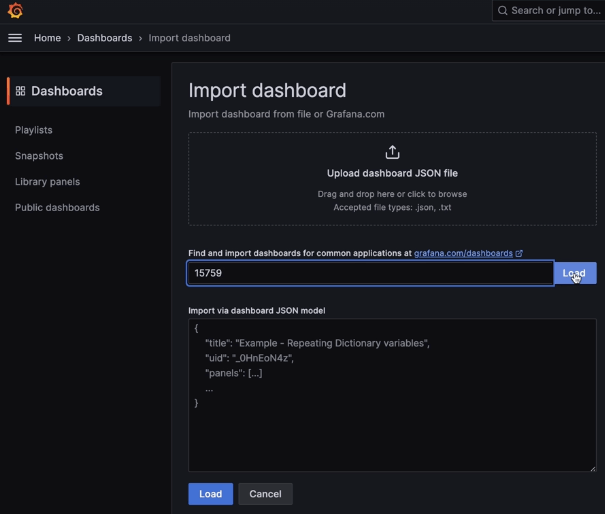
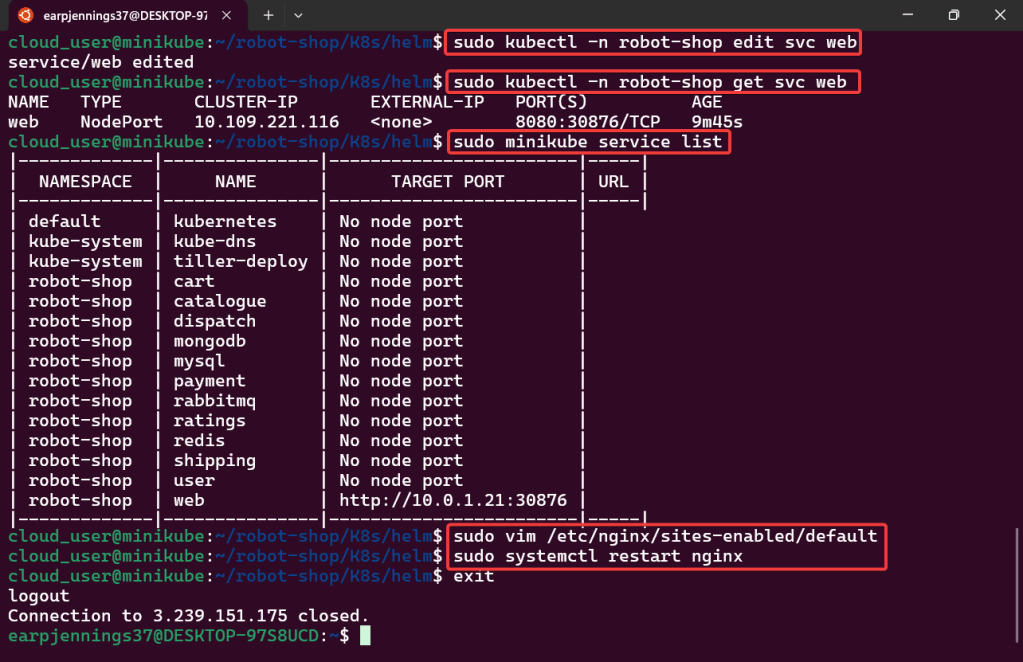
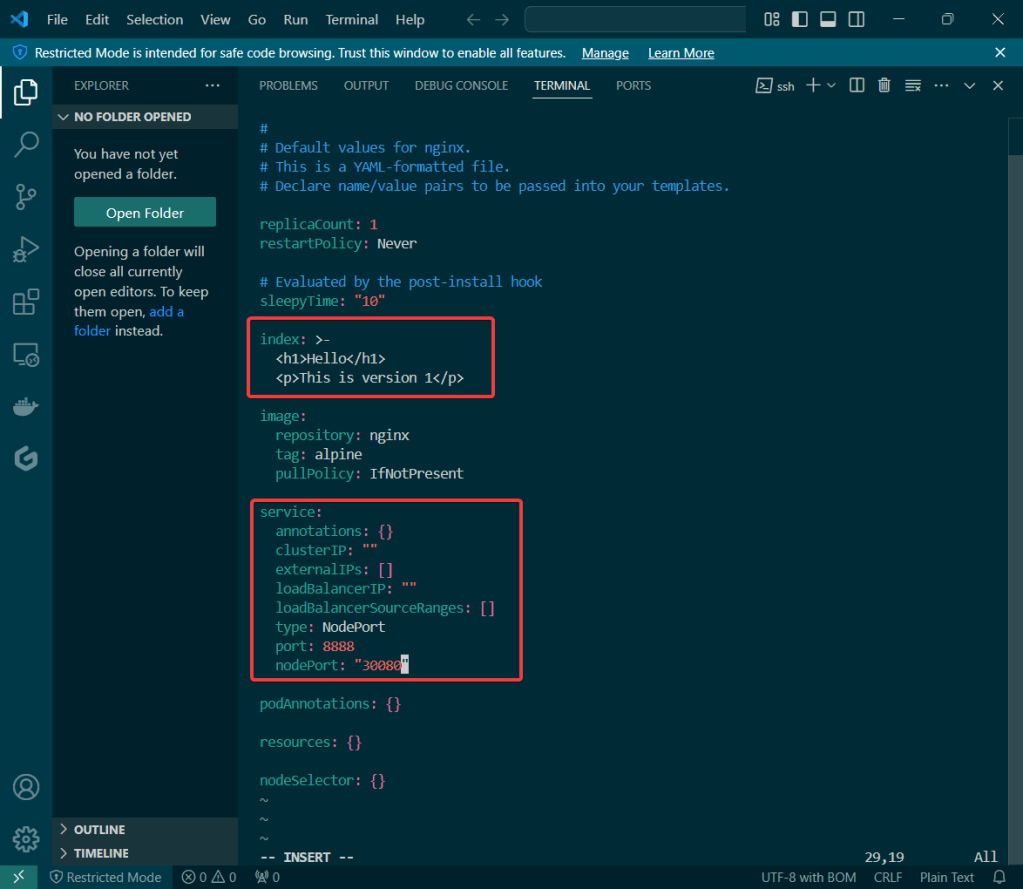
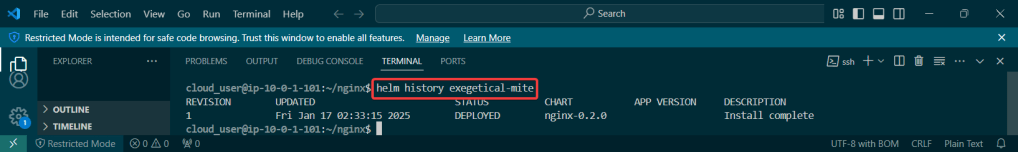
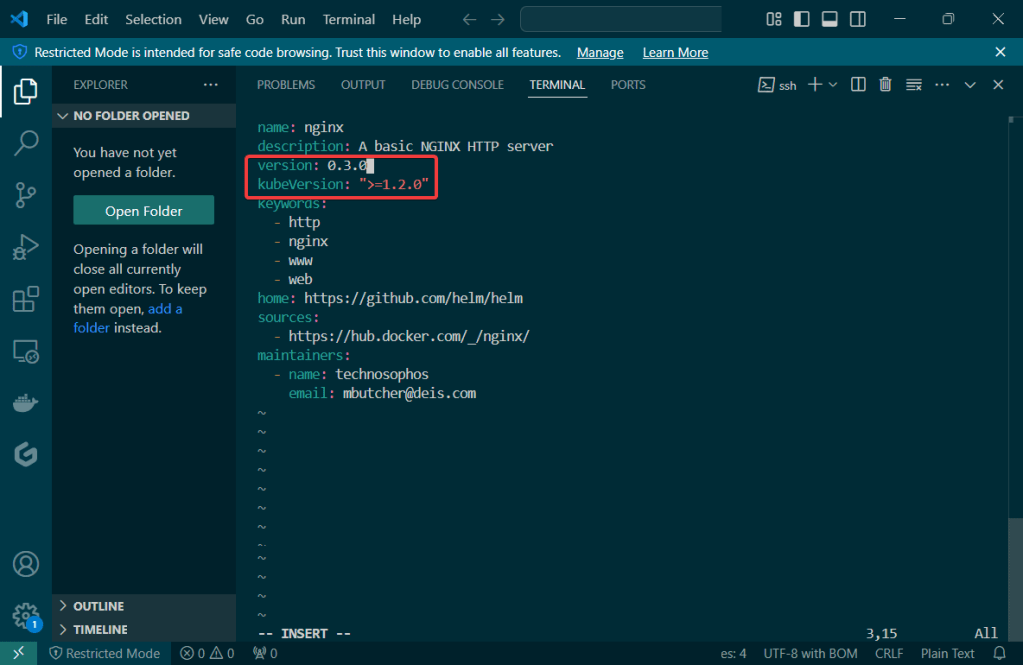
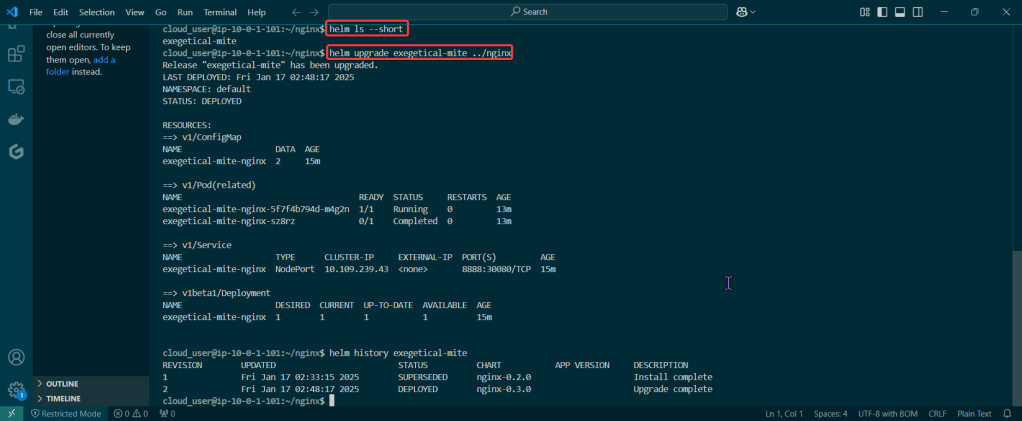
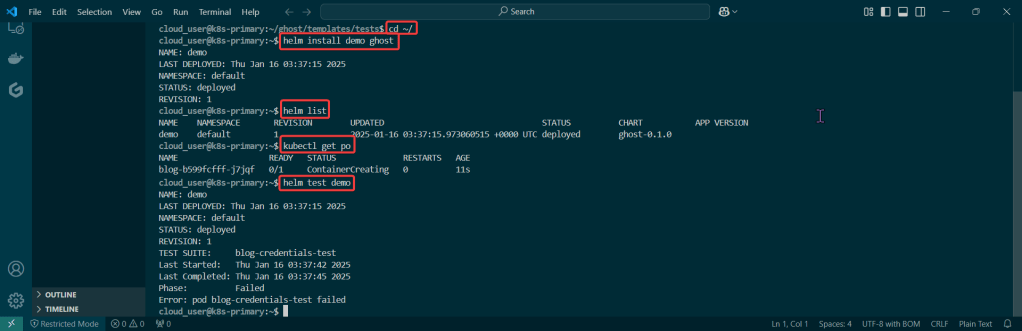
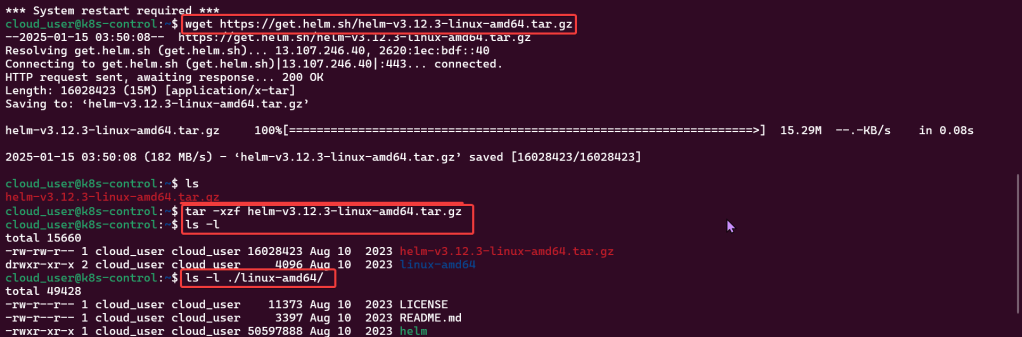
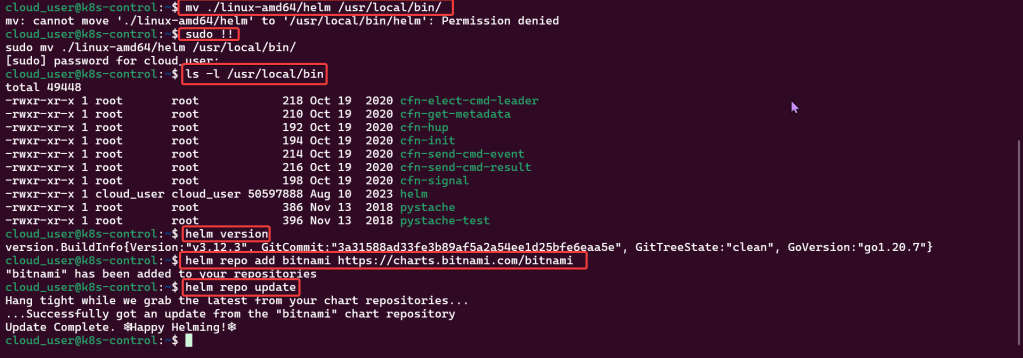
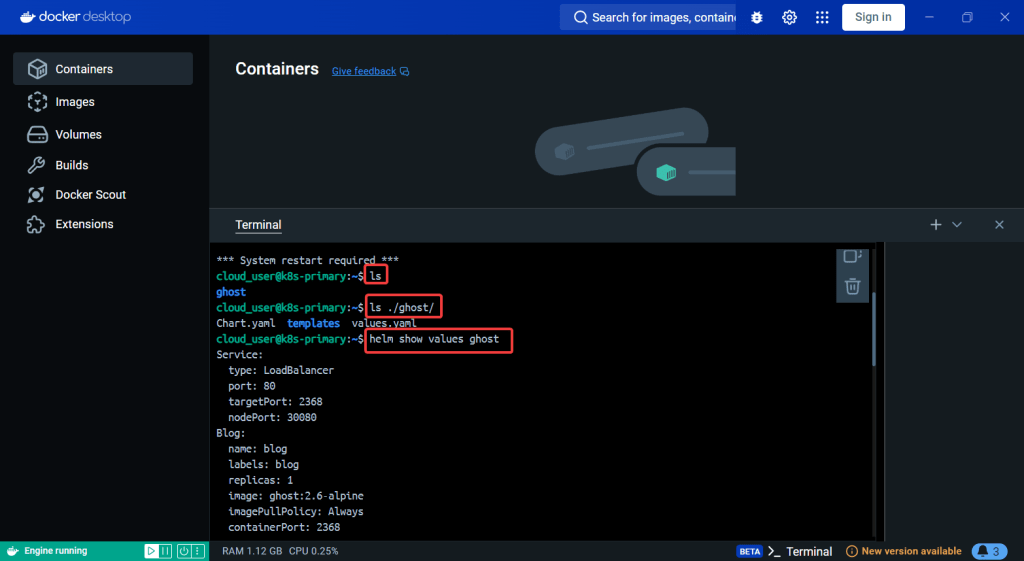
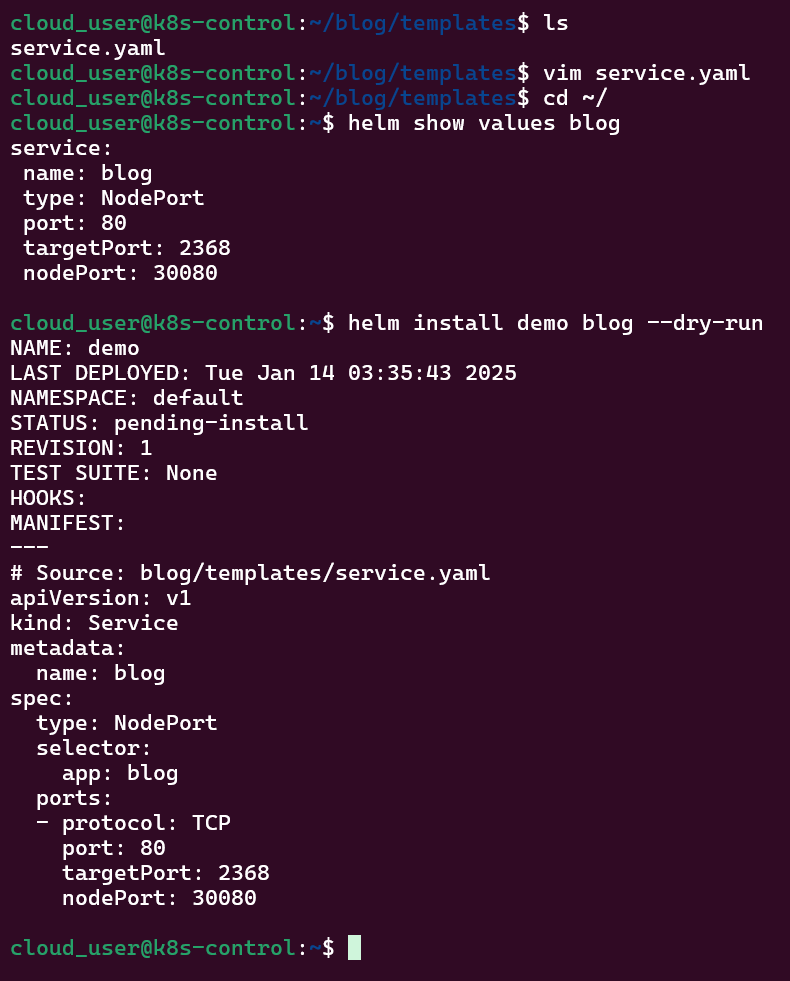
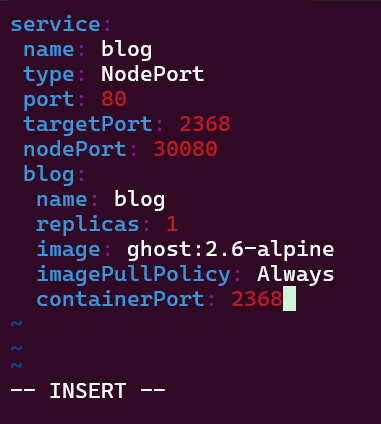
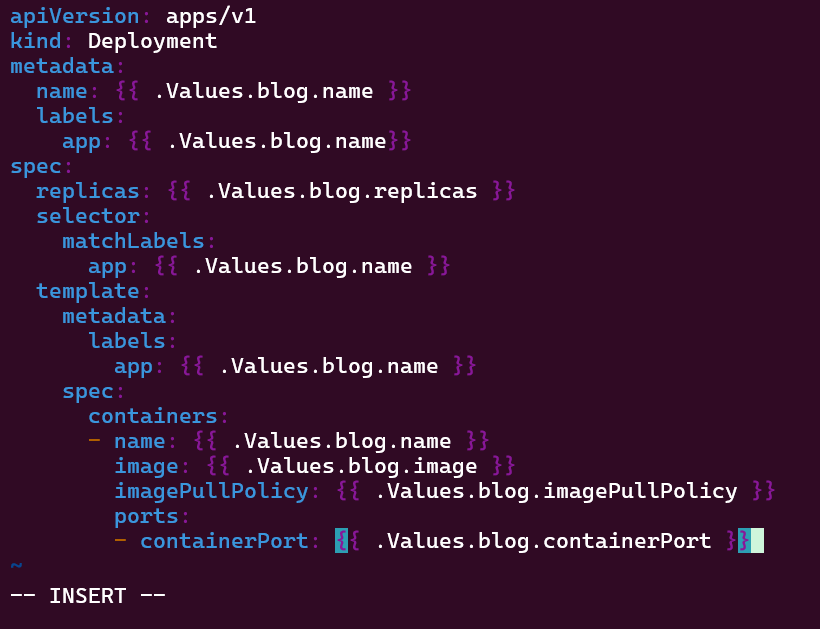
Helm Chart install:
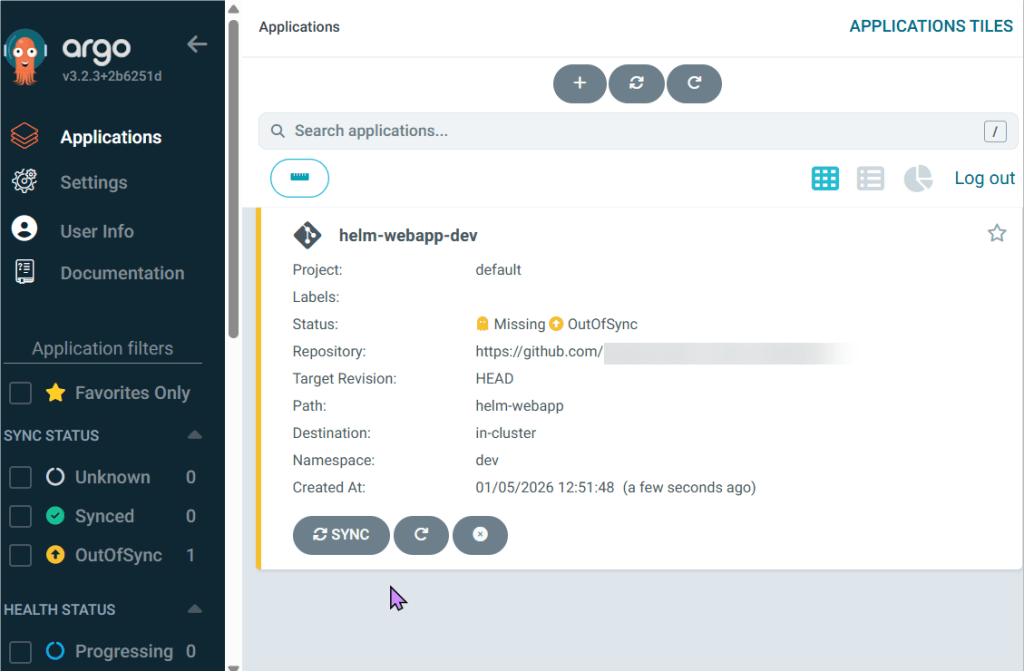

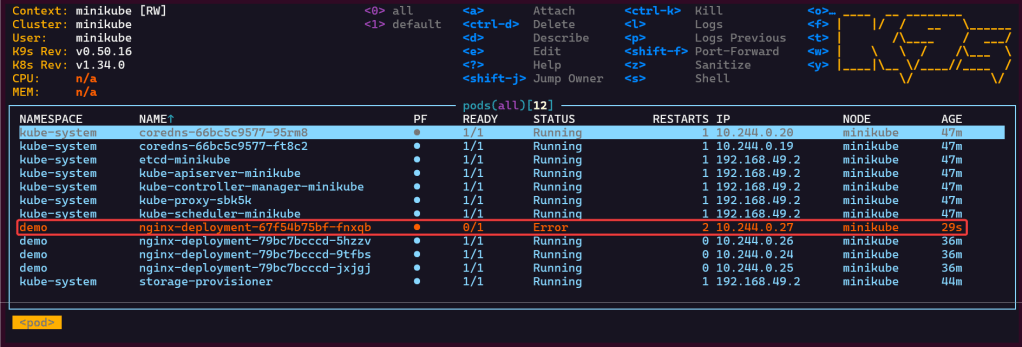
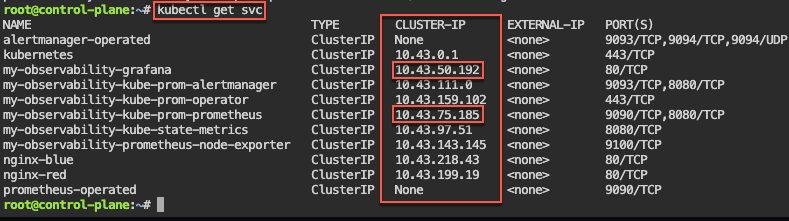
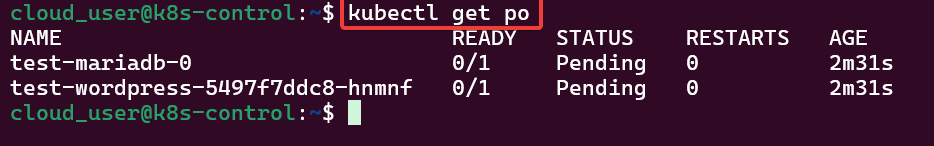
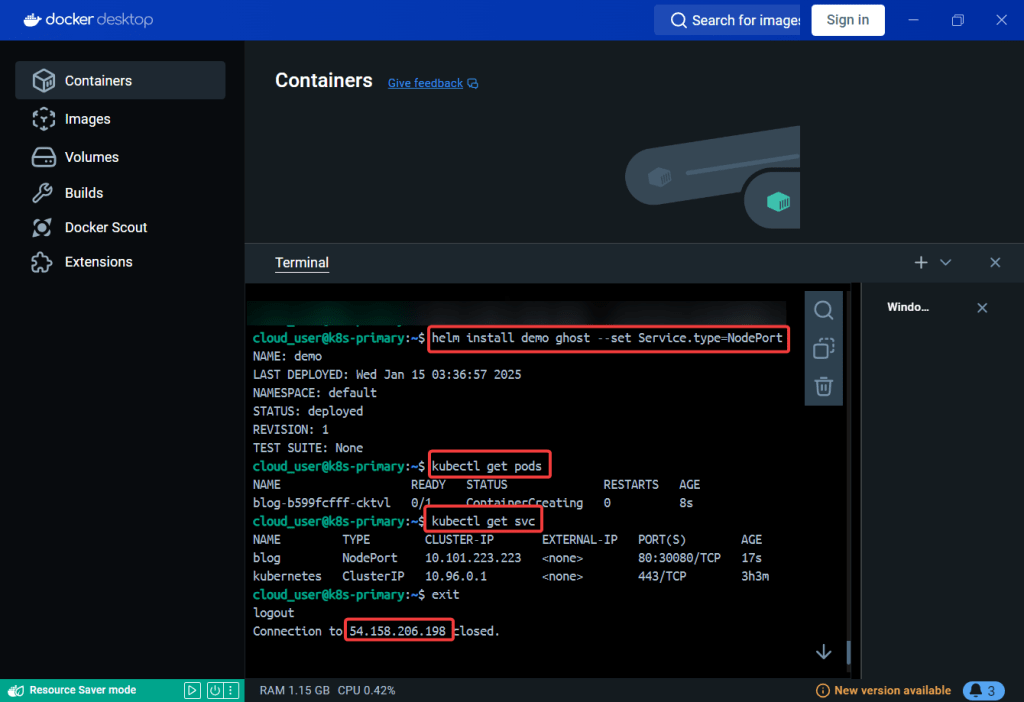
- See pods in k9s
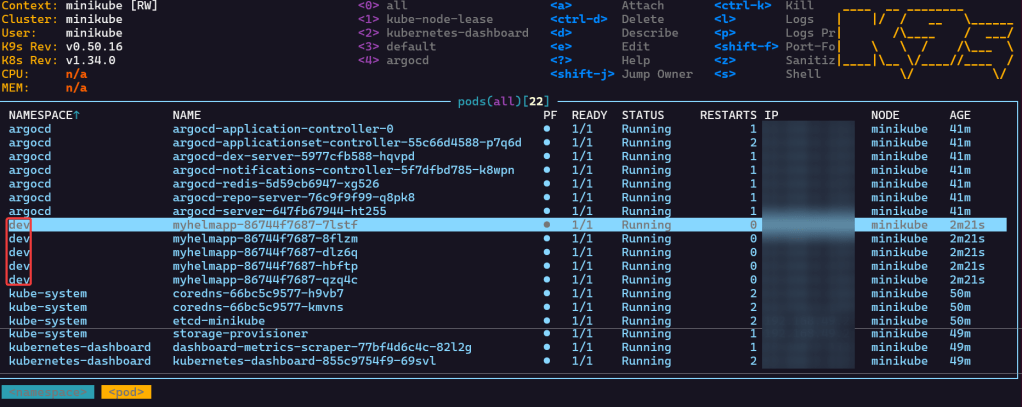
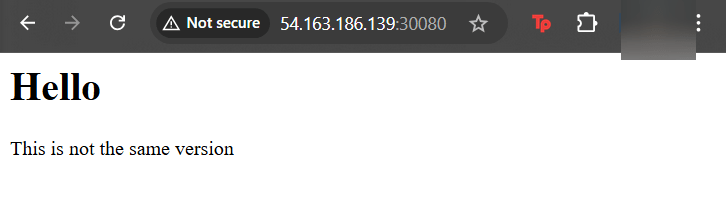
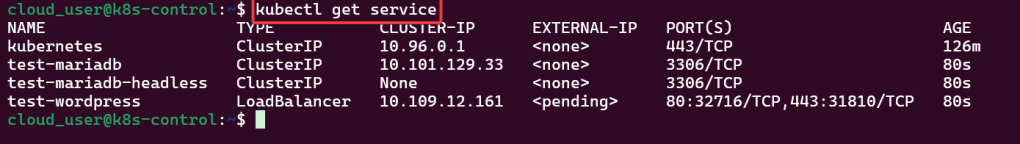
- Port-forward to 8888


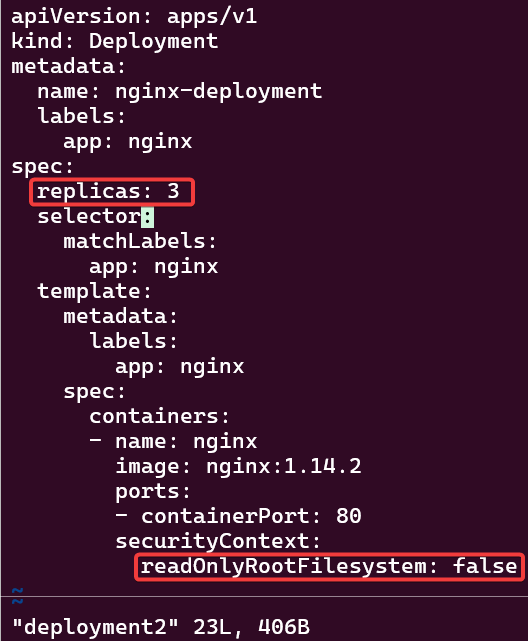
Scale-Up Replicas to 10:
- Update your github file & commit
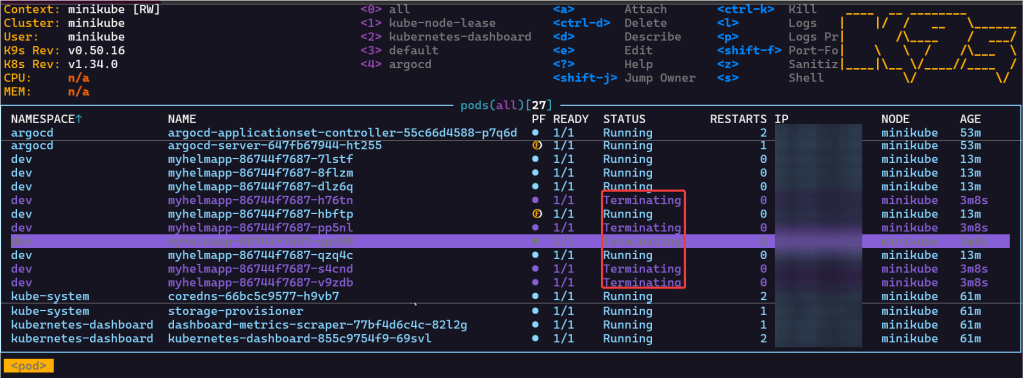
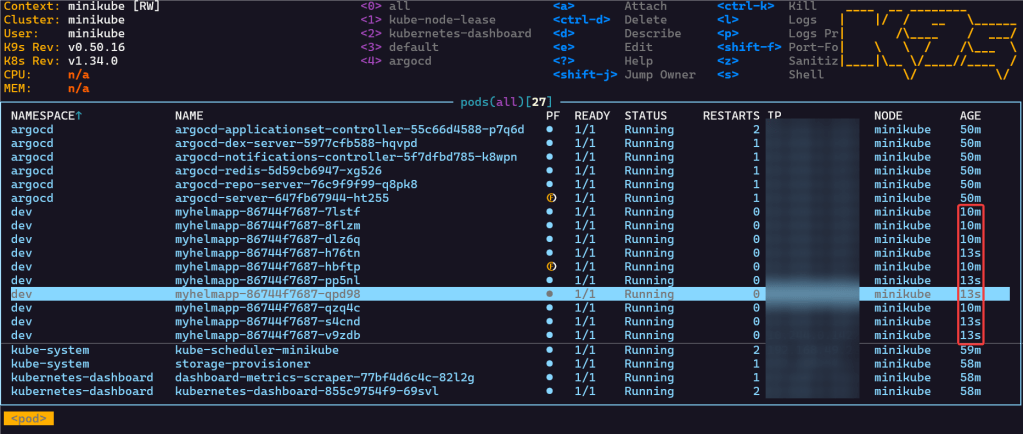
- Watch MAGIC..or “agentic-ai” – whatever you wanna call it
- Notice in k9s the pods age
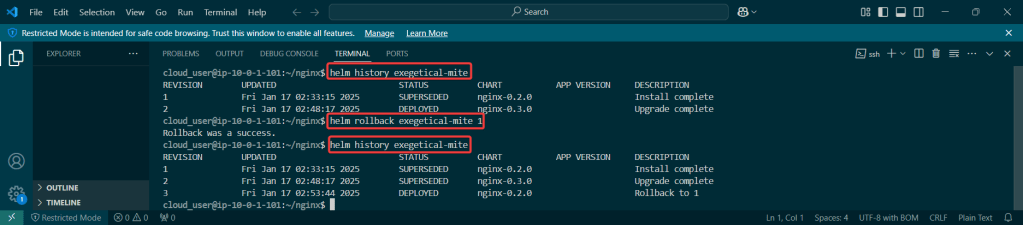
Rollback in ArgoCD
- For a quick fix cuz not sure what broke, can quickly go back instead of push more supposed changes/fixes from github
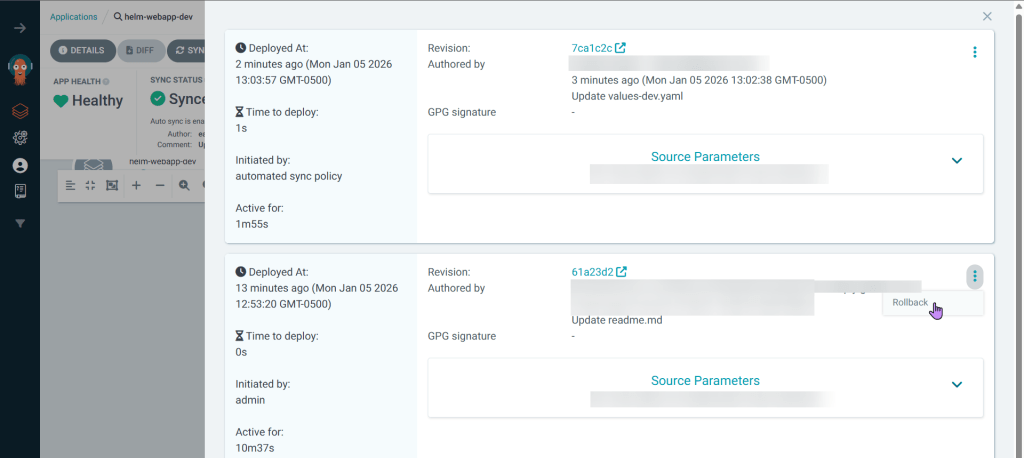
- Annnnnd see the termination of pods from the rollback in ArgoCD